文献:Lung cancer combination therapy: doxorubicin and β-elemene co-loaded, pH-sensitive nanostructured lipid carriers
文献链接:https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6498957/
作者:Chengsong Cao ,Qun Wang ,Yong Liu
相关产品:
mPEG-Hyd-DSPE 甲氧基聚乙二醇-腙键-磷脂
原文摘要:
Purpose: Co-delivery of drugs to achieve the synergistic anticancer effect is a promising strategy for lung cancer therapy. The purpose of this research is to develop a doxorubicin (DOX) and β-elemene (ELE) co-loaded, pH-sensitive nanostructured lipid carriers (DOX/ ELE Hyd NLCs).
Methods: In this study, DOX/ELE Hyd NLCs were produced by a hot homogenization and ultrasonication method and used for lung cancer treatment. In vitro and in vivo efficiency as well as toxicity of the system was evaluated on lung cancer cell lines and lung tumor-bearing mice.
Results: DOX/ELE Hyd NLCs had a particle size of 190 nm, with a PDI lower than 0.2. DOX/ELE Hyd NLCs exhibited a significantly enhanced cytotoxicity (drug concentration causing 50% inhibition was 7.86 μg/mL), synergy antitumor effect (combination index lower than 1), and profound tumor inhibition ability (tumor inhibition ratio of 82.9%) compared with the non pH-responsive NLCs and single-drug-loaded NLCs.
Conclusion: Since the synergistic effect of the drugs was found in this system, it would have great potential to inhibit lung tumor cells and tumor growth.
mPEG 和 DSPE 通过化学键连接形成 mPEG-DSPE。这种连接方式使得 mPEG-DSPE 兼具了 mPEG 的亲水性和 DSPE 的脂质特性,形成了一种具有两亲性的分子结构。mPEG-DSPE 具有很强的自组装能力。在水溶液中,由于其两亲性结构,分子会自发地聚集形成各种纳米结构,如胶束和脂质体。在自组装过程中,DSPE 部分形成内部的疏水区域,而 mPEG 部分则伸展在外部与水相接触,形成亲水性的外壳。这种自组装结构对于包裹疏水性化合物或其他生物活性分子非常有利。mPEG-Hyd-DSPE的酰腙键在酸性环境中会断裂,从而触发包裹化合物的释放。这种特性使得mPEG-Hyd-DSPE能够在tumor微环境或细胞内的溶酶体等酸性环境中释放化合物,实现化合物的准确递送和增强效果。DOX/ELE Hyd NLC指的是多柔比星(DOX)和β-榄香烯(ELE)共同负载的pH敏感纳米结构脂质载体(Nanostructured Lipid Carrier)。mPEG-Hyd-DSPE和mPEG-DSPE在许多方面有应用,例如在DOX/ELEHydnlc制备的过程中。
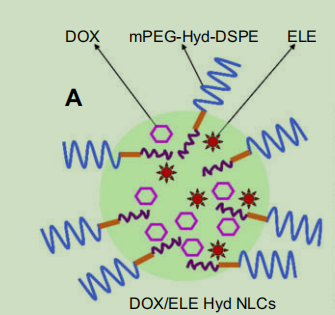
图为:纳米结构脂质载体(DOX/ELE Hyd NLCs)的方案图
mPEG-Hyd-DSPE在DOX/ELEHydnlc制备中的应用:
采用热均质法和超声法制备了DOX/ELEHydNLCs。首先,将DOX·HCl与等量摩尔比的TEA在DMSO中搅拌过夜,得到DOX碱。将复合醇®888 ATO和米甘醇®812混合,加热至融化;然后将DOX和ELE加入到混合物中,搅拌形成油相。将mPEG-Hyd-DSPE、卵磷脂和Tween®80溶解在水中中,并加热至以得到水相。然后将水相加入油相中,在振幅下使用超声检测。然后用冰水浴将混合物冷却。敏感的Hyd(DOX/ELE NLCs),采用相同的方法,使用mPEG-DSPE代替mPEG-HydDSPE制备。采用相同的方法制备DOX单药ph敏感NLCs(DOX Hyd NLCs),使用DOX,不添加ELE。采用相同的方法制备ELE单药ph敏感NLCs(NLCs,ELEHydNLCs),使用ELE,不添加DOX。采用相同的方法制备空白ph敏感NLCs(Hyd NLCs),不添加ELE和DOX。将DOX·HCl分离于ELE注射液制备DOX和ELE注射液(DOX/ELE INJ)。
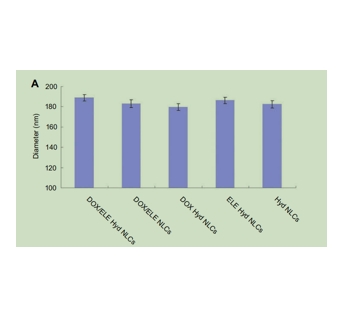
图为:NLCs的粒径
结论:DOX/ELE Hyd NLCs在该系统中具有协同作用,具有对肺tumor细胞和tumor生长的抑制潜力。使用含有mPEG-Hyd-DSPE的酸敏感肼(Hyd)键设计了ph敏感的纳米载体。NLCs含有ph可分裂的mPEG-Hyd-DSPE,它在细胞外腔室的中性生理条件下应该是稳定的。在进入pH降低的环境后,如一些tumor的细胞外空间,预计该复合物会在ph敏感的肼键分裂后释放更多的化合物。体外释放试验结果表明,pH敏感的DOX/ELE Hyd NLCs释放速度迅速。这可能是ph敏感的nlc可以被酸性pH触发并更快地从载体释放化合物的证据。

 2025-02-12 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-12 作者:lkr 来源:

