文献:Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Basedon Electrospun Biomimetic ScaffoldMediated Endothelial DifferentiationFacilitating Regeneration and Repairof Abdominal Wall Defects viaHIF-1α/VEGF Pathway
作者:Wenpei Dong, Zhicheng Song, Suihong Liu, Ping Yu, Zhipeng Shen,Jianjun Yang, Dongchao Yang, Qinxi Hu, Haiguang Zhangand Yan Gu
相关产品:PNIPAAm-b-PEG(聚(N - 异丙基丙烯酰胺)-b-聚乙二醇)
原文摘要:
Application of synthetic or biological meshes is the main therapy for the repair and reconstruction of abdominal wall defects, a common disease in surgery. Currently,no ideal materials are available, and there is an urgent need to find appropriate ones to satisfy clinical needs. Electrospun scaffolds have drawn attention in soft tissue reconstruction. In this study, we developed a novel method to fabricate a composite electrospun scaffold using a thermoresponsive hydrogel, poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly (ethylene glycol), and a biodegradable polymer, polylactic acid (PLA). This scaffold provided not only a high surface area/volume ratio and a three-dimensional fibrous matrix but also high biocompatibility and sufficient mechanical strength,and could simulate the native extracellular matrix and accelerate cell adhesion and proliferation. Furthermore, rat adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) were seeded in the composite electrospun scaffold to enhance the defect repair and regeneration by directionally inducing ADSCs into endothelial cells. In addition, we found early vascularization in the process was regulated by the hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway. In our study, overexpression of HIF-1α/VEGF in ADSCs using a lentivirus system promoted early vascularization in the electrospun scaffolds. Overall, we expect our composite biomimetic scaffold method will be applicable and useful in abdominal wall defect regeneration and repair in the future.
PNIPAAm-b-PEG:PNIPAAm(聚(N - 异丙基丙烯酰胺)):是一种温敏性聚合物。它的分子链中含有亲水性的酰胺基团和疏水性的异丙基。在一定温度范围内,其物理性质会发生明显变化。这个温度被称为低临界溶解温度(LCST)。当温度低于 LCST 时,PNIPAAm 分子链伸展,表现出良好的亲水性,能与水充分混合;当温度高于 LCST 时,分子链发生卷曲,聚合物变得疏水性增强,会从水溶液中析出。这种温敏特性使其在化合物递送、生物传感器等众多领域有广的应用。PEG是一种具有良好水溶性、生物相容性和低poison性的聚合物。在这个共聚物结构中,PEG 链段与 PNIPAAm 链段相连,能赋予材料新的性质。基于PNIPAAm-b-PEG的性能,仿生支架的制作如下:
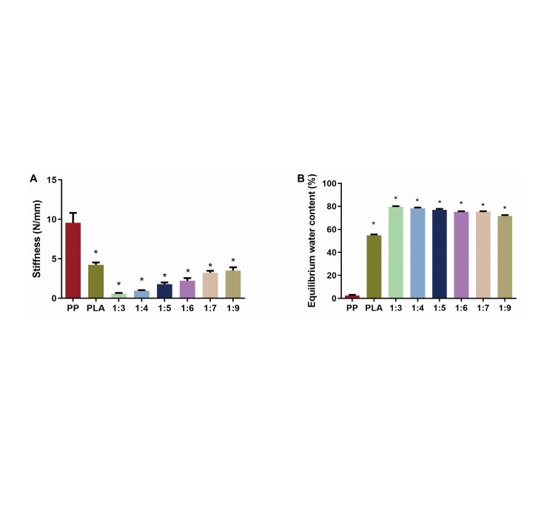
图:产品性能评价
仿生支架的制作:
为获得仿生支架,使用了3D打印辅助静电纺丝系统。物理混合PNIPAAm-b-PEG /PLA复合溶液。使用一定的内径针,并安装在静电纺丝系统上。纳米纤维以固定电势旋转。静电纺丝过程在一段时间完成,在接收平台上形成纳米纤维膜。最后,将电纺丝纳米纤维膜撕裂,放入烘箱中进一步蒸发,并干燥。此外,采用不同重量比的PNIPAAm-b-PEG和PLA制备仿生支架以作对比。
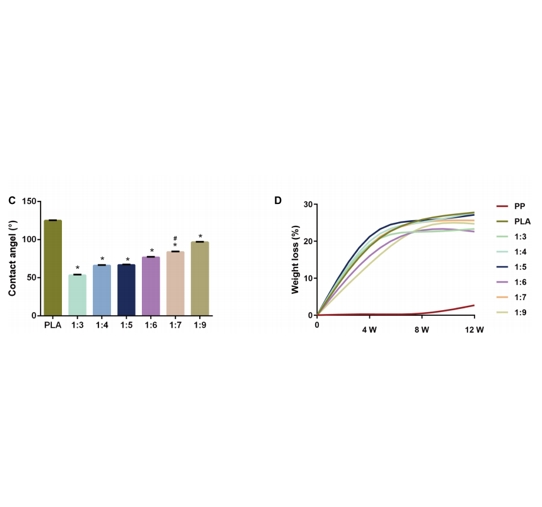
图:仿生支架性能评价
结论:
该文献成功制备出基于PNIPAAm-b-PEG合成的仿生支架。该支架不仅具有高表面积/体积比和三维纤维基质,而且具有高的生物相容性和足够的机械强度,可以模拟天然细胞外基质,加速细胞粘附和增殖。

 2025-02-12 作者:ws 来源:
2025-02-12 作者:ws 来源:

