文献:Engineering Biomimetic Platesomes for pH-Responsive Drug Delivery and Enhanced Antitumor Activity
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31222856/
作者:Guangna Liu, Xiao Zhao, Yinlong Zhang, Junchao Xu, Jiaqi Xu, Yao Li, Huan Min, Jian Shi, Ying Zhao, Jingyan Wei, Jing Wang,,Guangjun Nie
相关产品:DSPE-PEOz2000 磷脂-聚(2-乙基-2-噁唑啉)2000
原文摘要:Biomimetic camouflage, i.e., using natural cell membranes for drug delivery, has demonstrated advantages over synthetic materials in both pharmacokinetics and biocompatibility, and so represents a promising solution for the development of safe nanomedicine. However, only limited efforts have been dedicated to engineering such camouflage to endow it with optimized or additional properties, in particular properties critical to a “smart” drug delivery system, such as stimuli-responsive drug release. A pH-responsive biomimetic “platesome” for specific drug delivery to tumors and tumor-triggered drug release is described. This platesome nanovehicle is constructed by merging platelet membranes with functionalized synthetic liposomes and exhibits enhanced tumor affinity, due to its platelet membrane–based camouflage, and selectively releases its cargo in response to the acidic microenvironment of lysosomal compartments. In mouse cancer models, it shows significantly better antitumor efficacy than nanoformulations based on a platesome without pH responsiveness or those based on traditional pH-sensitive liposomes. A convenient way to incorporate stimuli-responsive features into biomimetic nanoparticles is described, demonstrating the potential of engineered cell membranes as biomimetic camouflages for a new generation of biocompatible and efficient nanocarriers.
DSPE-PEOz,DSPE 代表 1,2-二硬脂酰-sn-甘油-3-磷酸乙醇胺。它是一种磷脂,分子结构包含一个甘油骨架,连接着两个硬脂酸(一种长链脂肪酸)的酯键,以及一个磷酸乙醇胺头部基团。这种结构使 DSPE 具有疏水性的长链脂肪酸部分和亲水性的头部基团,在形成脂质双层结构(如脂质体)中发挥关键作用,是构成细胞膜模拟结构的重要成分。PEOz 是聚(2-乙基-2-噁唑啉)(Poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline))的缩写。它是一种具有良好生物相容性的聚合物,分子链由 2-乙基-2-唑啉单体聚合而成。PEOz 的化学性质比较特殊,它在不同的环境条件下可以表现出亲水性和温度响应等特性。与 DSPE 连接后,能够为整个分子带来新的物理化学性质。引用的文献中介绍了一种脂质体样载体,将血小板膜与传统脂质体融合,形成混合膜囊泡(平板体)。在此融合过程中,将一种对ph值敏感的脂质DSPE-PEOz加入到高原小体中,以使化合物在酸性环境中加速释放。
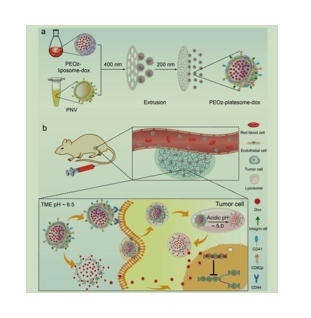
图为:peoz-平板-dox的制备及其抗tumor机制示意图
功能化仿生纳米载体:
采用梯度离心法从雌性BALB/c小鼠的全血中分离出血小板。膜通过冻融过程提取,并在低温保存直到使用。为了制造dox负载、ph敏感的杂交血小板体(peoz-dox),首先通过纯化的血小板膜超声制备血小板膜纳米囊泡(PNVs)。采用传统的膜复水化法制备了含有ph响应性脂质DSPE-PEOz(PEOz-脂质体-dox)的dox封装脂质体。然后将PEOz-脂质体-dox与PNV共挤压产生PEOz-平板体-dox。由于ζ电位分析表明,当PNV/PEOz-脂质体的比例增加时,产物混合平板体的表面电荷已经相当接近纯化血小板膜。这种表面电荷与合成的豌豆脂质体的表面电荷的转移也可能意味着这两种结构之间的成功融合。在低温的磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)中,dox也显示出令人满意的稳定性,一段时间后其水动力直径和表面电荷没有变化。通过透射电镜(TEM)观察,脂质体和平板体(PEOzplame体和peoz-dox)纳米颗粒均表现出典型的磷脂双层结构。
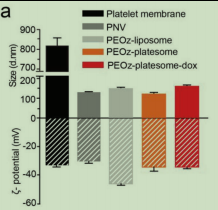
图为:聚氧化霉酶的表征
DSPE-PEOz加入到高原小体中得到的脂质体样载体,这种平板纳米载体是通过将血小板膜与功能化合成脂质体合并而成的,由于其基于血小板膜的伪装,表现出增强的tumor亲和力,并选择性地释放溶酶体室的酸性微环境响应其货物。在小鼠cancer模型中,它显示出基于无pH反应的平板或基于传统ph敏感脂质体的纳米制剂的抗tumorTherapeutic effect 明显优于纳米制剂。

 2025-02-12 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-12 作者:lkr 来源:

