文献:Ilexsaponin A1: In vitro metabolites identification and evaluation of inhibitory drug-drug interactions
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34461570/
作者:Liang Wu, An Kang , Xiaoliang Jin , Yuqing Bao , Peng Miao , Tingmei Lv ,Zhu Zhou ,
相关产品:UDP-glucose
原文摘要:As a triterpene saponin, ilexsaponin A1 is one of the most abundant, representative and active components in plants of Ilex pubescens, used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. This study aimed to identify the metabolites of ilexsaponin A1 and evaluate its in vitro inhibitory drug-drug interaction (DDI) potential by using human liver microsomes (HLM) and cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs)-specific probes, with all the qualitative and quantitative analysis performed by LC-MS/MS. As a result, two metabolites generated through the metabolic pathways of glucuronic acid conjugation and glucose conjugation were first time detected in the HLM. An inhibitory DDI evaluating system consisting of 7 major CYP enzymes involving 8 CYP-catalyzed reactions was established, validated and then used for the DDI evaluation. Our data suggested ilexsaponin A1 and its metabolite, ilexgenin A, are not direct or mechanism-based inhibitors of CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2D6, 2E1 or 3A4/5 at 0.05e10 mM. A significant decreased remaining activity of CYP2B6 (from 77.89 % to 23.19 %) was observed in a dose-dependent manner when increased the concentration of ilexsaponin A1 from 50 to 500 mM. Collectively, our data demonstrate ilexsaponin A1 is unlikely to cause DDIs by inhibiting co-administered drugs metabolized by these CYP enzymes.
UDP-glucose(尿苷二磷酸葡萄糖)是一种重要的生物分子,它在生物化学和生物学领域具有关键作用。UDP-glucose在体内由尿苷二磷酸葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶催化合成,该反应需要葡萄糖-1-磷酸和尿苷三磷酸作为底物,并生成焦磷酸作为副产物。储存时,UDP-glucose需要密封并在-20℃下保存,以确保其稳定性和活性。硅氧皂苷A1是一种三萜皂苷,是毛竹在Treatment 心Blood vessels疾病的植物中丰富、具代表性、活跃的成分之一。采用人肝微粒体(HLM)和细胞色素P450酶(CYPs)特异性探针,利用LC-MS进行体外抑制化合物-化合物相互作用(DDI)潜力,并采用LC-MS/MS进行定性和定量分析。
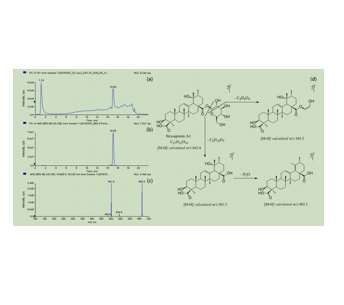
图为:苯环皂苷A1的代表性色谱、质谱和提出的破碎途径
UDP-glucose在HLM代谢稳定性研究和代谢酶鉴定中的应用:
采用HLM方法进行体外代谢稳定性研究和代谢酶鉴定。在代谢稳定性研究中,苯环皂苷A1的孵育浓度取等分。空白试验不含苯环糖皂苷A1,阴性对照试验不含HLM、NADPH再生系统和UDPGA。在选定的时间间隔收集空白和阴性对照试验的系列样本。
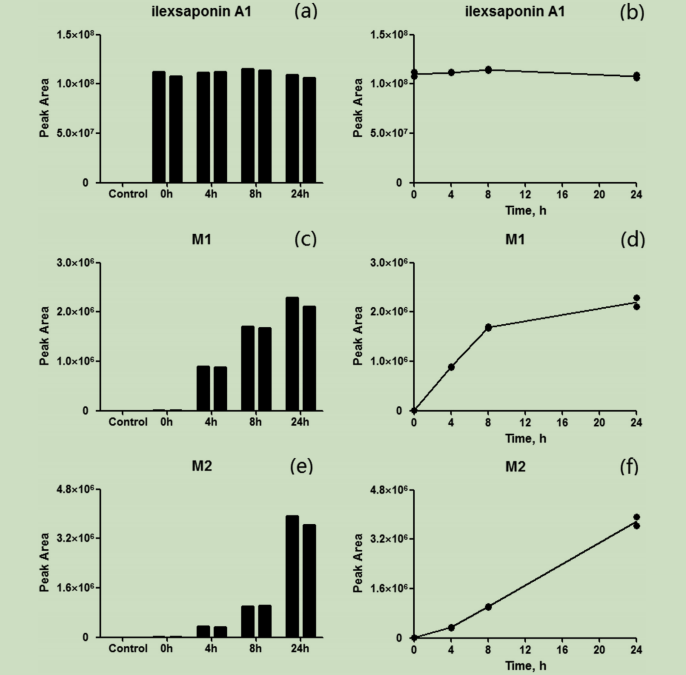
代谢稳定性研究与代谢酶鉴定:
当与微粒体孵育时,化合物浓度没有损失,这表明环外皂苷A1在常规HLM孵育系统中是代谢稳定的。与预期的一样,在空白对照中没有观察到来自基质或仪器的明显干扰;而在阴性对照试验中,苯环糖皂苷A1稳定。随着udp-葡萄糖的存在,M1的生成减少。在苯环皂苷A1到M2的酶催化过程中,NADPH再生系统和UDPGA似乎都是必要的,因为观察到的峰面积比在正常和阴性测定之间没有明显差异。当将Udp-葡萄糖添加到孵育系统时,观察到M2的形成增加。
图为:(a、b)苯环糖皂苷A1、(c、d)M1和(e、f)M2在HLM孵育系统(n¼2)中的峰面积-时间曲线
结论:采用常规HLM孵育系统,环己皂苷A1在体外的潜在生物转化。虽然苯外皂苷A1在HLM中稳定,但它们产生了两种代谢物,并随着培养时间的推移而积累。除了与葡萄糖醛酸(M1)结合的常见的代谢途径外,还发现了一种葡萄糖偶联物(M2)。将苯环皂苷A1与HLM共孵育,并鉴定并首次报道了苯环皂苷A1的两种偶联代谢物。与原型反应相比,偶联反应产生的两种代谢物会增加极性,减少保留时间,这可能有助于将硅外皂苷a1从体内清除。

 2025-02-12 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-12 作者:lkr 来源:

