文献:Combination Nanotherapeutics for Dry Eye Disease Treatment in a Rabbit Model
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34079253/
作者:Liandi Huang,Huanhuan Gao,Zhigang Wang ,Yixin Zhong ,Lan Hao ,Zhiyu Du
相关产品:Cholesterol 胆固醇
原文摘要:
Purpose: Anti-inflammation is essential for dry eye disease. Traditional anti-inflammation agent corticosteroids applied in dry eye disease (DED) treatment could result in high intraocular pressure, especially in long-term treatment. Thus, we have prepared a liposome loading1-bromoheptadecafluorooctane and tetrandrine (PFOB@LIP-Tet) to treat DED via anti-inflammation that hardly affects intraocular pressure in this study, which provided another therapy strategy for dry eye disease.
Methods: We firstly detected the physicochemical properties of PFOB@LIP-Tet. Next, we tested the biosafety of synthesized liposomes for corneal epithelium. Then, we explored the accumulations and distribution of PFOB@LIP-Tet both in cellular and animal models. And then, we assessed the therapeutic effects of PFOB@LIP-Tet formulations by laboratory and clinical examinations. Last, we examined the changes in eye pressure before and after treatment.
Results: PFOB@LIP-Tet and Tet showed a characteristic absorption peak at 282 nm while PFOB@LIP did not. Large amounts of PFOB@LIP-Tet remained on the ocular surface and accumulated in the corneal epithelial cells in DED rabbits. Corneal staining scores of DED rabbits respectively treated by ATS, PFOB@LIP-ATS, Tet-ATS and PFOB@LIP-Tet-ATS for seven days were 3.7±0.5, 3.2±0.4, 1.5±0.5 and 0.5±0.5. The expressions of related cytokines were correspondingly downregulated significantly, indicating that the inflammation of DED was successfully suppressed. The intraocular pressure changes of DED rabbits before and after treatment by PFOB@LIP-Tet showed no statistical significance.
Conclusion: We successfully synthesized PFOB@LIP-Tet, and it could effectively treat dry eye disease via anti-inflammation but hardly affected the intraocular pressure.
Cholesterol存在于动物细胞膜中,是动物细胞质膜的重要成分,动物细胞器膜的含量相对较少。在血液中,Cholesterol主要以Cholesterol酯的形式存在,约70%的Cholesterol与长链脂肪酸构成胆固醇酯。胆固醇是细胞膜的重要组成成分,约占细胞膜脂质成分的20%-25%,有助于维持细胞膜的流动性和通透性。PFOB@LIP-Tet制剂是一种针对DEDTreatment 的创新药物制剂,结合了脂质体作为药物载体、全氟溴辛烷(PFOB)作为靶向和定位Inflammation区域的成分,以及汉防己甲素(Tet,也称为粉防己碱)作为抗炎活性成分。PFOB@LIP-Tet制剂具有特定的粒径、电位和形态等理化性质。
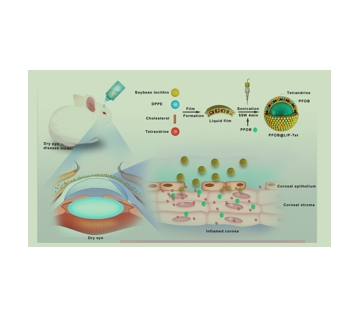
图为:PFOB@LIP-Tet的合成示意图及Treatment 过程。
Cholesterol在PFOB@LIP-Tet脂质体合成中的应用:
PFOB@LIP-Tet合成通过传统薄膜分散超声振荡方法:大豆卵磷脂、DPPE、胆固醇,测试,均匀溶解在三氯甲烷,然后蒸发旋转蒸发器直到一个均匀的液体薄膜形成。然后用PBS溶解,然后加入PFOB。最后,用超声器在冰浴中进行超声振荡获得PFOB@LIP-Tet,然后离心。取出上清液,收集沉积物,用PBS或人工撕裂替代液重悬。
脂质体理化性质的观察:
采用紫外分光光度计检测游离Tet、PFOB@LIP和PFOB@LIP-Tet的吸收光谱。在透射电镜(TEM)下观察了PFOB@LIP-Tet和PFOB@LIP的形貌。用莫尔文粒度分析仪检测平均尺寸、多分散指数(PDI)和表面电位。PFOB@LIP-Tet检测时间延长的平均大小。此外,还用数码照片记录了大体外观差异。

图为:PFOB@LIP-Tet配方产品的性能数码照片(1 mg/mL)
结论:PFOB@LIP-Tet在生物安全性和控释性方面优于Tet。作为药物载体,脂质体长期以来一直因被包裹的分子泄漏和自动解体而受到批评,但利用脂质体的特性实现了Tet和PFOB的释放,而不施加额外的力量。假设已经得到证实,传统的脂质体PFOB@LIP-Tet在DED角膜上皮上有明显的积累。与PFOB结合并加载到脂质体上后,Tet的抗炎功能增强,其对眼压的影响降低。PFOB@LIP-Tet可通过抗炎药有效Treatment 干眼症,这是通过抑制VEGF、IL-1β、TNF-α和PEG2的表达和释放来实现的,但对眼压影响不大。此外,随着泪膜屏障的繁荣,PFOB@LIP-Tet的作用将逐渐减弱。

 2025-02-10 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:lkr 来源:

