文献:Programmable antibiotic delivery to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus through precision therapy
文献链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168365920301383
作者:Shaoqi Qu, Ying Liu,Qiao Hu,Yiming Han,Zhihui Hao,JianzhongShen, Kui Zhu
相关产品:
Dextran-RBITC 葡聚糖-红色荧光素罗丹明
原文摘要:The rapid dissemination of life-threatening multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens calls for the development of new antibacterial agents and alternative strategies. The virulence factor secreted by bacteria plays a crucial role in the sophisticated processes during infections. Inspired by the unique capacity of many bacteria inducing clotting of plasma to initiate colonization, we propose a programmable antibiotic delivery system for precision therapy using methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) as a model. Coagulase utilized by MRSA to directly cleave fibrinogen into fibrin, is an ideal target not only for tracking bacterial status but for triggering the collapse of fibrinogen functionalized porous microspheres. Subsequently, staphylokinase, another virulence factor of MRSA, catalyzed hydrolysis of fibrin to further release the encapsulated antibiotics from microspheres. Our sequential triggered-release system exhibits high selectivity to distinguish live or dead MRSA from other pathogenic bacteria. Furthermore, such programmable microspheres clear 99% MRSA in 4 h, and show increased efficiency in a wound healing model in rats. Our study provides a programmable drug delivery system to precisely target bacterial pathogens using their intrinsic enzymatic cascades. This programmable platform with reduced selective stress of antibiotics on microbiota sheds light on the potential therapy for future clinical applications.
PLL链上的氨基使其整体带正电荷,能够与带负电荷的生物分子(如DNA、RNA、细胞膜等)发生静电相互作用。PLL具有良好的生物相容性,与细胞和组织之间的相互作用温和,适用于生物医学应用。PLL在体内可以被酶解成单体L-赖氨酸,这些单体是人体必需的氨基酸之一,因此PLL具有良好的生物降解性和生物安全性。PLL可以形成稳定的薄膜,并具有较强的粘附性,适用于涂层、封装和固定化等应用。构建一个系统,利用germ固有的酶级联来可编程释放抗生素。多层聚电解质功能化多孔微球核装载万古霉素(记为PMS)。将万古霉素(Van)嵌入多孔聚(乳酸共乙醇酸)(PLGA)微球(MS)中,表面进一步包裹纤维蛋白原和聚(l)赖氨酸。

图为:可编程PMS对MDRbacteria的生物反应过程示意图
PLL在聚电解质多层微球制造中的应用:
采用水油水双乳液法制备多孔PLGA微球(MS)。PLGA和BSA分别溶解于二氯甲烷和去离子水中。将PVA水溶液倒入混合物(PLGA和BSA溶液的乳液)中,使用匀浆器在再次乳化形成双乳液。蒸发有机溶剂,将双乳液倒入PVA水溶液中,在室温下继续混合。固化后的微球用去离子水洗涤三次并进行冻干。对于装载右旋糖酐−RBITC或Van的微球,在加入PLGA溶液之前,将右旋糖酐−RBITC或Van加入到BSA溶液中。为了制备聚电解质多层微球,基于静电相互作用,将聚电解质层涂覆在多孔微球上。将的多孔微球溶液分散在PLL溶液中,然后在收集微球,用氯化钠洗涤,然后依次沉积下一层。沉积后获得聚电解质多层微球(PMS),并保存在MES中,直至使用。用BCA蛋白检测试剂盒测定微粒上包覆的纤维蛋白原的含量。
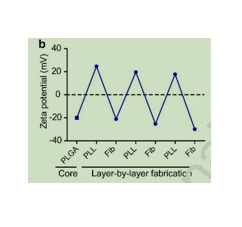
图为:Fib和聚(l-赖氨酸)(PLL)功能化的PMS的zeta电位的分层转化。
结论:PLL多聚赖氨酸在聚电解质多层微球制造中的应用具有优势和潜力。通过利用PLL多聚赖氨酸的独特特性,可以制备出具有良好的性能和稳定性的聚电解质多层微球。随着对PLL多聚赖氨酸研究的深入和制备技术的不断发展,其在生物医学和纳米领域中的应用将会更加深入,也需要注意到PLL多聚赖氨酸在应用过程中可能存在的问题和挑战,如制备过程的复杂性、药物释放的可控性等。

 2025-02-10 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:lkr 来源:

