文献:Construction and comparison of different nanocarriers for co-delivery of cisplatin and curcumin: A synergistic combination nanotherapy for cervical cancer
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28027539/
作者:Changming Li, Xiangcheng Ge, Liguo Wang
相关产品:
原文摘要:
Purpose: Co-delivery of two or more drugs into the same cancer cells or tissues in the same nanocarriers provides a new paradigm in cancer treatment. In this study, two kinds of nanocarriers: lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNs) and polymeric nanoparticles (PNPs) were constructed and compared for co-delivery of cisplatin (DDP) and curcumin (CUR).
Methods: DDP and CUR loaded LPNs (D/C/LPNs) and PNPs (D/C/PNPs) were prepared. Two kinds of nanocarriers were characterized in terms of particle size, zeta potential, drug encapsulation efficiency (EE), and drug release. Their in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo anti-tumor efficacy was studied on human cervix adenocarcinoma cell line (HeLa cells) and mice bearing cervical cancer model.
Results: Compared with D/C/PNPs, D/C/LPNs showed significantly higher cytotoxicity in vitro. D/C/LPNs also displayed the best antitumor activity than other formulations tested in vivo.
Conclusions: The results demonstrated that LPNs could improve the anticancer efficacy of drugs to higher levels than PNPs and free drugs, thus could serve as an effective drug system for targeted and synergistic co-delivery nanomedicine for cervical cancer chemotherapy.
PEG-DSPE是聚乙二醇(PEG)与二硬脂酰磷脂酰乙醇胺(DSPE)的结合产物。这种结合使得PEG-DSPE既具有PEG的亲水性和生物相容性,又具备DSPE的磷脂特性,从而被应用于药物输送、纳米颗粒制备和生物医学研究中。脂质聚合物纳米粒(LPNs)是一种结合了脂质体和聚合物纳米粒优点的新型纳米递药系统。由于LPNs具有生物相容性和稳定性,能够减少药物在体内的降解和代谢,从而降低药物的有害副作用。等离子体纳米颗粒(PNPs)是一种具有独特物理、化学、光学和生物学特性的纳米材料。它们的光学性质可以通过调节其大小、组成、形貌和微环境来进行控制。PNPs的独特之处在于其局域表面等离子体共振(LSPR)特性,这一特性使得它们能够在单颗粒水平上进行实时成像和分析。
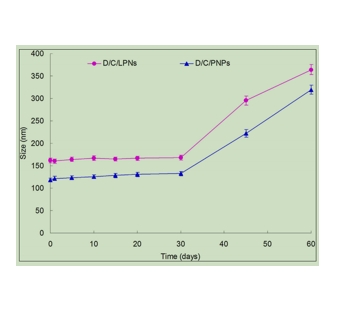
图为:D/C/LPNs和D/C/PNPs的平均直径
PEG-DSPE在LPNs和PNPs制备过程中的应用:
采用纳米共沉淀技术制备了D/C/lpn。其中,PLGA,DDP和CUR溶解于二甲亚砜中。将卵磷脂和与PLGA溶解在乙醇中,并在搅拌下加热。同时分别将PLGA溶液滴加入脂质溶液中。然后将溶液旋转。将混合物在室温下搅拌。采用透析方法去除有机溶剂:透析与Milli-Q水一起透析。最后离心,每次洗涤几次,得到D/C/lpn。在单一药物存在的情况下,采用相同的方法制备DDP装载LPNs(D/LPNs)和CUR装载LPNs的LPNs(C/LPNs)。同时制备无药物的空白lpn作为对照。DDP和CUR负载PNPs(D/C/PNPs)的制备方法为: PLGA、DDP和CUR溶解在二甲亚砜中。将有机相滴加到所需的F68(w/v)的水稳定剂中,在室温下搅拌。采用透析方法去除有机溶剂:用Milli-Q水透析。最后,通过多次洗涤混合物得到D/C/PNPs。同时制备无药物的空白PNPs作为对照。
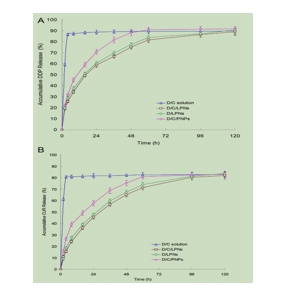
图为:从lpn、pnp和解决方案中释放DDP (A)和CUR (B)
结论:采用纳米共沉淀技术制备了LPNs和PNPs 。该方法的优点是操作简单,能耗低。此外,它通常会导致合成粒子的狭窄分布和容易分散。这种方法特别有利于将亲脂性药物掺入纳米颗粒中,从而提高了传递系统的EE性。D/C/LPNs的尺寸大于D/C/PNPs。这可以用lpn的脂质壳来解释,这使得颗粒的尺寸大于PNPs。D/C/lpn和D/C/PNPs的表面电荷均为负电荷。lpn的zeta电位低于PNPs。这是因为带负电荷的PLGA链和PEG链。纳米载体的表面负电荷可以降低系统有害性。两种药物的包封对纳米颗粒的EE和DL没有影响,单载药载体的影响无明显差异。

 2025-02-10 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:lkr 来源:

