文献:
Assessment of proliferation, migration and differentiation potentials of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells labeling with silica-coated and amine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
文献链接:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32394163/
作者:
Dong Yao , Na-na Liu,Bi-wen Mo
相关产品:
SPIO@SiO2-NH2 磁性纳米颗粒@二氧化硅-氨基
原文摘要:
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have been widely used for cell labeling in preclinical and clinical studies, to improve labeling efficiency, particle conjugation and surface modifications are developed, but some modified SPIONs exert side-effect on physiological activity of cells, which cannot be served as ideal cell tracker. In this study, amine-modified silica-coated SPIO (SPIO@SiO2-NH2, SPIO@S-N) nanoparticles were used to label bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs), then the stem cell potentials were evaluated. It was found BM-MSCs could be efficiently labeled by SPIO@S-N nanoparticles. After labeling, the BMMSCs viability kept well and the migration ability increased, but the osteogenesis and adipogenesis potentials were not impaired. In steroid associated osteonecrosis (SAON) bone defect model, stem cell implantation was performed by injection of SPIO@SN labeled BM-MSCs into marrow cavity locally, it was found the SPIO positive cells homed to the periphery of defect region in control group, but were recruited to the defect region in poly lactic-coglycolic acid/tricalcium phosphate (PLGA/TCP) scaffold implantation group. In conclusion, SPIO@S-N nanoparticles promoted migration while retained proliferation and differentiation ability of BM-MSCs,implying this kind of nanoparticles could be served not only an ideal tracking marker but also an accelerator for stem cell homing during tissue repair.
SPIO@SiO₂- NH₂是一种核-壳结构的纳米复合材料。核心部分是超顺磁性氧化铁(SPIO),外壳是二氧化硅(SiO₂),并且二氧化硅外壳上修饰有氨基(- NH₂)。超顺磁性氧化铁(SPIO)具有特殊的磁性。其内部的铁离子(Fe³⁺和 Fe²⁺)排列方式使得它在没有外加磁场时,磁矩随机取向,整体不显磁性;而在施加外加磁场时,磁矩会迅速沿磁场方向排列,表现出很强的磁性。这种超顺磁性在磁分离、磁共振成像(MRI)等技术中非常重要。二氧化硅(SiO₂)外壳起到了保护核心 SPIO 的作用,同时提供了一个稳定的表面用于后续的功能化修饰。二氧化硅具有良好的化学稳定性、生物相容性和易于修饰的特点。氨基(- NH₂)是一种活性官能团,它的存在使得该纳米复合材料可以与其他含有活性基团(如羧基、醛基等)的分子发生化学反应,从而实现更多功能的拓展。该文献基于此合成SPIO@S-N纳米颗粒:
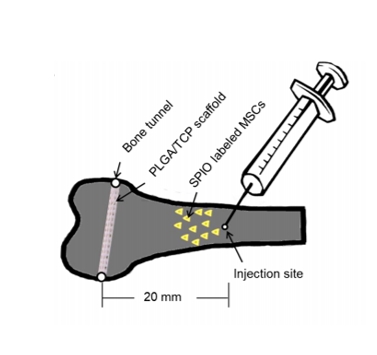
图:作用机制
第一步:功能化二氧化硅壳层表面:利用 SPIO@SiO₂ - NH₂表面的氨基(- NH₂)与含硫化合物进行反应。如果使用硫醇(R - SH)作为硫源,可能会发生氨基与硫醇的缩合反应,例如,通过适当的活化剂(如碳二亚胺类化合物)促进反应,这个反应可以在纳米颗粒表面引入硫基团。
第二步:构建含氮新壳层或对硫修饰后的壳层进行氮掺杂:以乙二胺(H₂N - CH₂ - CH₂ - NH₂)为例,如果要构建新的壳层,可以将其与经过硫修饰后的纳米颗粒进行反应。乙二胺中的氨基可能会与其他活性基团(如剩余的未反应的硫醇基团或者新生成的其他活性基团)发生反应,形成含有氮的新壳层。如果是进行氮掺杂,乙二胺可以在一定的反应条件下(如高温、等离子体等条件)与硫修饰后的纳米颗粒表面发生反应,将氮原子引入到壳层结构中。

图:对照图像
结论:
该文献成功制备了基于SPIO@SiO2-NH2合成的SPIO@S-N纳米颗粒。结果发现,SPIO@S-N纳米颗粒可以有效地标记骨髓间充质干细胞。标记后,骨髓间充质干细胞活力保持良好,迁移能力增强,但成骨和脂肪生成潜能未受损。综上,SPIO@S-N纳米颗粒在促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移的同时,保留了增殖和分化能力,意味着这种纳米颗粒可以作为跟踪标记。

 2024-12-19 作者:ws 来源:
2024-12-19 作者:ws 来源:

