文献:
A pH/ROS dual-responsive and targeting nanotherapy for vascular inflammatory diseases
文献链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961219307045作者:
Runjun Zhang, Renfeng Liu, Chao Liu, Lina Pan, Yuantong Qi, Juan Cheng, Jiawei Guo, Yi Jia, Jun Ding, Jianxiang Zhang, Houyuan Hu
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG-maleimide(磷脂-聚乙二醇-马来酰亚胺)
原文摘要:
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Vascular inflammation is closely related to the pathogenesis of a diverse group of CVDs. Currently, it remains a great challenge to achieve site-specific delivery and controlled release of therapeutics at vascular inflammatory sites. Herein we hypothesize that active targeting nanoparticles (NPs) simultaneously responsive to low pH and high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) can serve as an effective nanoplatform for precision delivery of therapeutic cargoes to the sites of vascular inflammation, in view of acidosis and oxidative stress at inflamed sites. The pH/ROS dual-responsive NPs were constructed by combination of a pH-sensitive material (ACD) and an oxidation-responsive material (OCD) that can be facilely synthesized by chemical functionalization of β-cyclodextrin, a cyclic oligosaccharide. Simply by regulating the weight ratio of ACD and OCD, the pH/ROS responsive capacity can be easily modulated, affording NPs with varied hydrolysis profiles under inflammatory microenvironment. Using rapamycin (RAP) as a candidate drug, we first demonstrated in vitro therapeutic advantages of RAP-containing NPs with optimal dual-responsive capability, i.e. RAP/AOCD NP, and a nonresponsive nanotherapy (RAP/PLGA NP) and two single-responsive nanotherapies (RAP/ACD NP and RAP/OCD NP) were used as controls. In an animal model of vascular inflammation in rats subjected to balloon injury in carotid arteries, AOCD NP could accumulate at the diseased site after intravenous (i.v.) injection. Consistently, i.v. treatment with RAP/AOCD NP more effectively inhibited neointimal hyperplasia in rats with induced arterial injuries, compared to RAP/PLGA NP, RAP/ACD NP, and RAP/OCD NP. By surface decoration of AOCD NP with a peptide (KLWVLPKGGGC) targeting type IV collagen (Col-IV), the obtained Col-IV targeting, dual-responsive nanocarrier TAOCD NP showed dramatically increased accumulation at injured carotid arteries. Furthermore, RAP/TAOCD NP exhibited significantly potentiated in vivo efficacy in comparison to the passive targeting nanotherapy RAP/AOCD NP. Importantly, in vitro cell culture experiments and in vivo animal studies in both mice and rats revealed good safety for AOCD NP and RAP/AOCD NP, even after long-term treatment via i.v. injection. Consequently, our results demonstrated that the newly developed Col-IV targeting, pH/ROS dual-responsive NPs may serve as an effective and safe nanovehicle for precision therapy of arterial restenosis and other vascular inflammatory diseases.
DSPE - PEG - maleimide 是一种功能性磷脂 - 聚乙二醇 - 马来酰亚胺化合物。其中 DSPE 代表 1,2 - 二硬脂酰 - sn - 甘油 - 3 - 磷酸乙醇胺(1,2 - distearoyl - sn - glycero - 3 - phosphoethanolamine),是一种磷脂成分。PEG 是聚乙二醇(polyethylene glycol),它起到连接和修饰的作用,能够增加化合物的水溶性和生物相容性等诸多性质。Maleimide(马来酰亚胺)是一种活性官能团,它可以与含有巯基(-SH)的分子发生特异性的化学反应。基于此,该文献制备具有响应性的物质pH/ROS双响应NPs流程如下:

图:响应机制
肽和iv型胶原的NPs的制备:
首先,使用PBS溶液,中性pH还原iv型胶原靶向肽(klwvlpkggc-Am)。然后在室温下,以DSPE-PEG-马来酰亚胺按一定的摩尔比,合成共轭的DSPE-PEG。通过透析过夜去除游离肽。然后采用上述方法,以OCD/ACD按一定的重量比,DSPE-PEG-肽/DSPE-PE按一定的摩尔比的混合物制备载肽和iv型胶原的NPs。
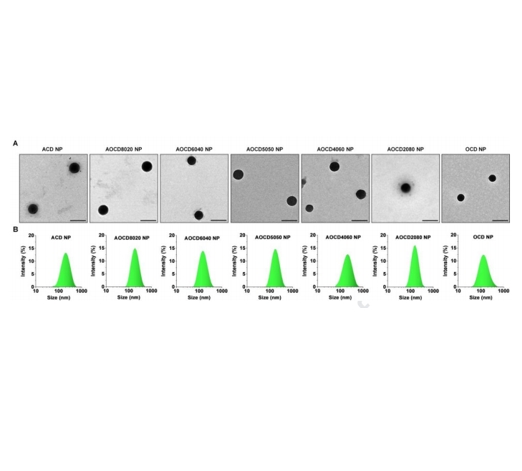
图:表征图像
结论:
该文献成功制备了基于DSPE-PEG-maleimide的pH/ROS双响应NPs材料,这种材料比传统脂质体和单ph响应脂质体提高,并能够容易地调节pH/ROS的响应能力,从而在微环境下提供具有不同水解谱的NPs。研究结果表明,新开发的Col-IV靶向,pH/ROS双响应NPs可能作为一种有效和安全的纳米载体。

 2024-12-18 作者:ws 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:ws 来源:

