文献:Modulation of Tumor Hypoxia by pH-Responsive Liposomes to Inhibit Mitochondrial Respiration for Enhancing Sonodynamic Therapy
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32821097/
作者:Nan Zhang,Yang Tan , Liwei Yan,Chunyang Zhang ,Ming Xu,Huanling Guo,Bowen Zhuang,Luyao Zhou ,Xiaoyan Xie
相关产品:DSPE-PEOz2000(磷脂-聚(2 -乙基- 2-噁唑啉)2000)
原文摘要:
Background and Purpose: Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) has been widely used for the noninvasive treatment of solid tumors, but the hypoxic tumor microenvironment limits its therapeutic effect. The current methods of reoxygenation to enhance SDT have limitations, prompting reconsideration of the design of therapeutic approaches. Here, we developed a tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoplatform by reducing oxygen consumption to overcome hypoxia-induced resistance to cancer therapy.Methods: A pH-responsive drug-loaded liposome (MI-PEOz-lip) was prepared and used to reduce oxygen consumption, attenuating hypoxia-induced resistance to SDT and thereby improving therapeutic efficiency. Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) and fluorescence imaging (FI) of MI-PEOz-lip were evaluated in vitro and in breast xenograft tumor models. The pHsensitive functionality of MI-PEOz-lip was applied for pH-triggered cargo release, and its capacity was evaluated. The MI-PEOz-lip-mediated SDT effect was compared with other treatments in vivo.Results: MI-PEOz-lip was demonstrated to specifically accumulate in tumors. Metformin molecules in liposomes selectively accumulate in tumors by pH-responsive drug release to inhibit the mitochondrial respiratory chain while releasing IR780 to the tumor area. These pH-responsive liposomes demonstrated PAI and FI imaging capabilities in vitro and in vivo, providing potential for treatment guidance and monitoring. In particular, the prepared MIPEOz-lip combined with ultrasound irradiation effectively inhibited breast tumors by producing toxic reactive singlet oxygen species (ROS), while the introduction of metformin inhibited mitochondrial respiration and reduced tumor oxygen consumption, resulting in excellent sonodynamic therapy performance compared with other treatments.Conclusion: In this study, we present a novel strategy to achieve high therapeutic efficacy of SDT by the rational design of multifunctional nanoplatforms. This work provides a new strategy that can solve the current problems of inefficient oxygen delivery strategies and weaken resistance to various oxygen-dependent therapies.
DSPE - PEOz2000 主要由两部分组成。DSPE(1,2 - 二硬脂酰 - sn - 甘油 - 3 - 磷酸乙醇胺)部分是一种磷脂。它包含一个磷酸乙醇胺的亲水性头部和两条硬脂酸的疏水性长链。这种结构使 DSPE 本身就具有一定的两亲性。PEOz2000 是指分子量约为 2000 的聚(2 - 乙基 - 2 - 噁唑啉),它连接在 DSPE 上。PEOz 链具有良好的亲水性,并且其化学结构赋予它一些物理化学性质,如良好的溶解性和生物相容性。基于DSPE - PEOz2000的优良性能,该文献相关脂质体制备流程如下:
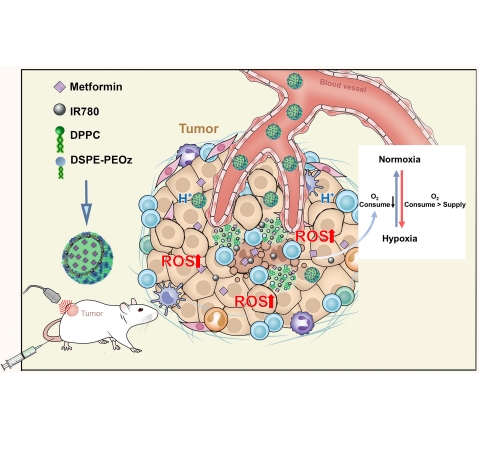
图:作用机制
MI-PEOz-lip是通过将DPPC、胆固醇、DSPE-PEOz和IR780溶解在含氯仿中的烧瓶中合成的。然后在水浴中旋转蒸发完全挥发。脂膜形成后,加入二甲双胍溶液,在适宜温度下超声一段时间。悬浮液通过过滤器过滤多次,装载ir780的磷脂在核心中与二甲双胍水溶液中形成脂质体。最终的MI-PEOz-lip产物用G-50 Sephadex柱纯化。二甲双胍和iR780脂质体(MI-PEG-lip,不含ph敏感磷脂)、IR780-ph敏感脂质体(IR780-PEOz-lip)和IR780脂质体(IR780-lip)。

图:对比曲线图
结论:
该文献成功制备出了基于DSPE-PEOz的脂质体,实验结果表明: 基于DSPE-PEOz的脂质体MI-PEOz-lip能在tumour中特异性积累并能联合超声照射通过产生有poison活性单线态氧(ROS)有效抑制tumour,而二甲双胍的引入抑制线粒体呼吸,减少tumour耗氧量,与其他相比具有良好的声动力性能。

 2024-12-18 作者:ws 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:ws 来源:

