文献:Ultrasound monitoring of magnet-guided delivery of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with magnetic lipid–polymer hybrid nanobubbles
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1w680py0yy3b04100d750230c9114591&site=xueshu_se
作者:Bo Zhang,Xinhai Mo, Fei Yu, Yuqin Ma and Fei Yan
相关产品:DSPE-PEG-FITC 磷脂-聚乙二醇-荧光素
原文摘要:Restenosis remains a pressing clinical problem that occurs in patients undergoing revascularization procedures, such as coronary artery bypass surgery and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Previous reports have proved that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) could effectively reduce the restenosis resulting from intimal hyperplasia following vascular injury. However, non-invasive delivery of MSCs and real-time monitoring of their retention at the site of vascular injury still remain a significant challenge. Therefore, we synthesized magnetic lipid–polymer hybrid nanobubbles (Mag-LPNs) as ultrasound contrast agents for cellular labeling of MSCs, endowing these MSCs with magnetic responsibility and real-time tracking capability by ultrasound. In order to enhance the internalization efficiency of MSCs, Mag-LPNs were modified
with cationic polymers to generate positively charged Mag-LPNs (P-Mag-LPNs). Intriguingly, the internalization of P-Mag-LPNs did not exhibit obvious harmful effects on the labeled MSCs in terms of cell viability and differentiation capacity. Moreover, the magnet-guided delivery of labeled MSCs in a rat carotid artery injury model developed using a 2-French balloon catheter could be tracked by ultrasound in a realtime manner. About 5-fold more MSCs were attached at the site of the injured artery with the aid of an external magnet field, compared with the absence of a magnet field. Herein, our study provides an innovative tracking platform for magnet-guided delivery of stem cells treating cardiovascular diseases.
DSPE - PEG - FITC从结构上看,它是由1,2 - 二硬脂酰 - sn - 甘油 - 3 - 磷酸乙醇胺(DSPE)、聚乙二醇(PEG)和异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)组成。DSPE具有良好的亲脂性,可与细胞膜等脂质结构相互作用。FITC是一种常用的荧光标记物,在特定波长的激发光下能发出明亮的荧光,方便对目标进行可视化观察和追踪。可用于标记脂质体、纳米颗粒等药物递送系统,使其在细胞摄取研究、体内分布监测等过程中能被清晰地识别和定位,也可用于标记细胞膜等生物结构以研究其相关生理过程。该文献用PLGA-PEG-RB和DSPE-PEG-FITC配制对细胞进行染色,然后在共聚焦激光扫描显微镜下观察,证明聚合物和脂质之间的空间关系。过程如下:
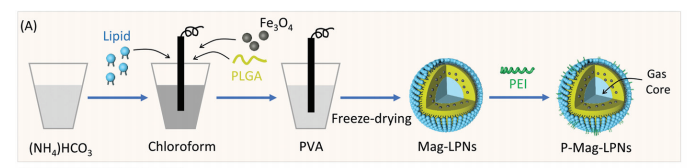
图:p-magg-lpn的制备示意图。
采用共聚焦激光显微镜扫描来验证P-Mag-lpn是否可以内化到MSCs中。简单地说,MSCs在玻璃底培养皿中培养,并与dii标记的P-Mag-LPNs加湿培养箱中孵育。轻轻清洗充质干细胞。然后,用小麦胚芽凝集素偶联DSPE-PEG-FITC(WGA-FITC)对细胞膜进行染色,细胞核用赫斯特33342染色。在共聚焦激光扫描显微镜观察标记的间充质干细胞并拍照。
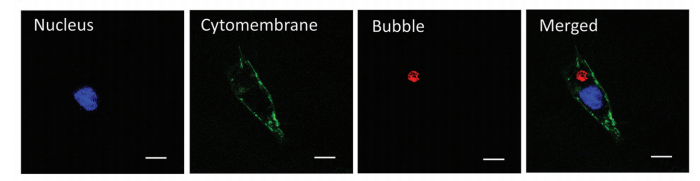
图:(C)用P-Mag-lpn标记的MSCs共聚焦激光扫描显微镜图像。质膜染成绿色(WGA-FITC),细胞核染成蓝色(Hoechst 33342),P-mag-LPNs染成红色(DiI)。
结论:DSPE - PEG - FITC在细胞生物学研究中,其亲脂性的DSPE部分能够轻易地插入到细胞质膜的脂质双分子层中,使与之相连的荧光标记FITC定位在膜上。这种特异性的定位使得细胞质膜在荧光显微镜下清晰可见。由于PEG链段的存在,不仅增加了整个分子在水溶液中的稳定性和溶解性,还减少了非特异性吸附,保证了染色的准确性。在活细胞实验中,它可以在不破坏细胞生理功能的情况下对细胞质膜进行染色,从而方便研究者观察细胞的形态、运动、融合等过程。同时,通过与其他标记技术或药物递送系统结合,还可以进一步研究膜相关的生理过程。

 2025-04-16 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-04-16 作者:ZJ 来源:

