原文献:
疏水改性普鲁兰多糖及其自组装载药纳米粒的研究
文献链接:
https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=16070840fd760cs08j7206y02k145372&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1
作者:
杨文智
原文摘要:
.Natural polysaccharides have hydrophilicity, stability, and biodegradability; At the same time, polysaccharide molecular chains have various types of functional groups, which can be modified by chemical and biochemical methods to obtain corresponding functionalized polysaccharide derivatives. Pluran polysaccharides are water-soluble, easily chemically modified with multiple hydroxyl groups, and lack immunogenicity, making them suitable as drug carriers. Endogenous cholesterol molecules have a cyclic structure and exhibit a certain degree of hydrophobicity. And succinic acid was chosen as the connecting arm to graft cholesterol onto the molecular chain of pullulan polysaccharide, obtaining amphiphilic cholesterol based pullulan (CHSP) and FITC labeled amphiphilic cholesterol based pullulan (FITC labeledCHSP) sugar derivatives.
Characterization of synthesized pullulan derivatives using infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), powder crystal diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer, and fluorescence spectrophotometer. The synthesis of amphiphilic cholesterol based pullulan was demonstrated through FT-IRNMR, XRD, and DSC experiments. Using CHSP and FITC as raw materials, FITC labeled CHSP was synthesized under the catalysis of dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) and characterized by FT-IR and HNMR. The FITC substitution degree of the derivative was calculated by NMR and fluorescence spectrophotometry, with 4.3 FITCs substituted per 100 sugar units. FITC labeled CHSP self aggregated gel nanoparticles were prepared by dialysis method. Characterization of the physicochemical properties of CHSP nanoparticles using HNMR, dynamic laser scattering (DLS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and steady-state fluorescence probe method. Due to the different degrees of cholesterol substitution of CHSP materials, self polymerized gel nanoparticles with particle size of 51.8~73 nm were obtained. There are no polar substituents in the CHSP molecular structure, and the absolute zeta potential of its nanoparticles in distilled water is approximately zero. The critical aggregation concentration (cac) of CHSP material is directly related to the degree of cholesterol substitution. As the degree of cholesterol substitution increases, the cac concentration decreases. FITC labeled CHSP self aggregated nanoparticles with a particle size of around 50 nm can be prepared using dialysis method.
Conclusion: Amphiphilic CHSP materials can form self aggregating gel nanoparticles in water and can be used as nano carriers to contain hydrophobic antiumor drug FITC labeled pullulan derivatives of CHSP; The experiment on Wistar rats showed that CHSP nanoparticles loaded with EPI can achieve long circulation and sustained release effects in rats; FITC labeled CHSP nanoparticles can be used as markers for introducing materials into cells, and co incubation with cells can effectively observe the process of nanoparticle entry.
天然多糖具有亲水、稳定、物可降解性;同时,多糖分子链有较多不同种类的基团,经化学和生化方法修饰,可获得相应的功能化多糖衍生物。普鲁兰多糖具有水溶性、多羟基易化学修饰和缺少免疫原性,可做药物载体。内源性胆固醇分子具有环状结构,其分子有一定的疏水性。而选择琥珀酸为连接臂将胆固醇接枝到普鲁兰多糖分子链上,获得两亲性胆固醇基普鲁兰(CHSP)和FITC标记的两亲性胆固醇基普鲁兰(FITC-labeledCHSP)糖衍生物。
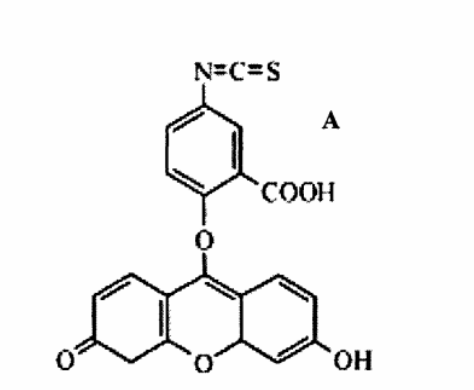
图:FITC结构式
通过FT-IRNMR、XRD和DSC实验证明,合成了两亲性胆固醇基普鲁兰。以CHSP和FITC为原料,在二月桂酸二丁基锡(DBTDL)催化下,合成FITC-labeled CHSP并经FT-IR和HNMR表征,通过NMR和荧光分光光度法计算衍生物的FITC取代度,每100糖单元取代4.3个FITC。通过透析法制备FITC-labeled CHSP自聚集水凝胶纳米粒。用'HNMR、动态激光散射(DLS)、透射电镜(TEM)和稳态荧光探针法对CHSP纳米粒物化性质进行表征。由于CHSP材料的胆固醇取代度不同,获得粒径在51.8~73 nm 自聚集水凝胶纳米粒。CHSP分子结构中无极性取代基,其纳米粒在蒸馏水中的zeta电位绝对值近似为零。而CHSP材料的临界聚集浓度(cac)的大小直接与胆固醇取代度有关,当胆固醇取代度增大,cac浓度减小。采用透析法可制备粒径在50 nmm左右的FITC-labeled CHSP自聚集纳米粒。
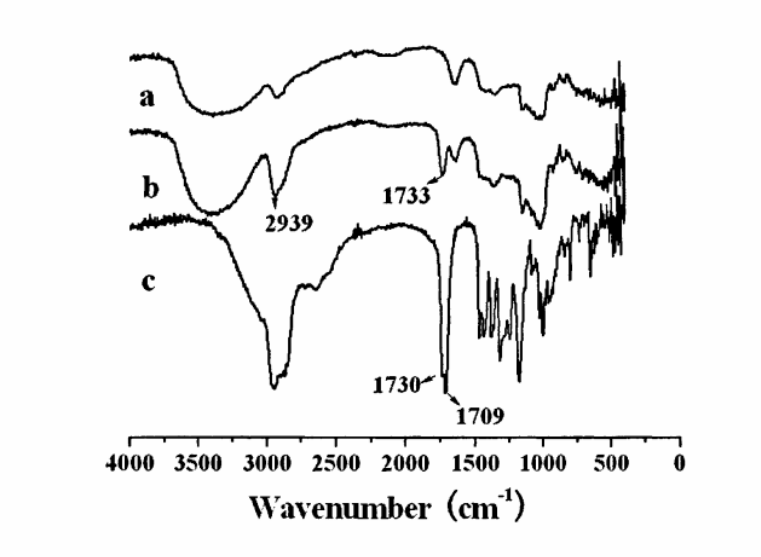
图:红外图谱分析(a)普鲁兰(b)CHSP(c)CHS
结论:两亲性CHSP材料可在水中形成自聚集凝胶纳米粒并可用作包载疏水性antitumor drug FITC 标记的CHSP的普鲁兰糖衍生物的纳米载体;wistar大鼠实验表明,包载EPI的CHSP纳米粒在大鼠体内能达到长循环和缓释作用;而FITC-labeled CHSP 纳米粒可用作材料导入细胞的标志物,用其纳米粒与细胞共孵育,可观测纳米粒入胞的过程。

 2024-12-18 作者:ZJ 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:ZJ 来源:

