文献:An iron oxide nanoparticle-based transdermal nanoplatform for dual-modal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy of superficial tumors
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=164e0v70x80s0gm0s9030gb0mb120551&site=xueshu_se
作者:Yuanyuan Zhang , Fenfen Li , Shengnan Ya , Yi Hu, Debo Zhi, Wenshen Wang ,
Mengran Xu, Bensheng Qiu, Weiping Ding
相关产品:
DDAB 双癸基二甲基溴化铵
DSPE-PEG2000-NHS 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-活性酯
原文摘要:Transdermal delivery is an attractive strategy for treating superficial tumors. However, the applications of existing transdermal systems have been limited by low transdermal efficiency and poor therapeutic outcomes. Here, we develop a transdermal nanoplatform (+)T-SiDs, based on superparamagnetic ironoxide core, surface-modified with cationic lipids, transdermal enhanced peptide TD, and 1,1’-dioctadecyl- 3,3,3’,3’-tetramethylindotricarbocyanine iodide (DiR), and loaded with doxorubicin. The (+)T-SiDs compositions enable MR/NIR dual-modal imaging guided synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy to superficial tumors treatment via transdermal delivery. The (+)T-SiDs exhibit good stability, efficient cellular uptake,
pH/photothermal responsive drug release, and high photothermal conversion efficiency (47.45%). Importantly, the transdermal delivery of (+)T-SiDs is significantly enhanced by TD functionalization. In vivo MR/NIR imaging shows that the (+)T-SiDs exhibit high transdermal efficiency and specificity in localization to the tumor site. Moreover, in comparison with individual chemo- or photothermal therapies, the combination of chemo-photothermal therapy exhibits more efficient tumor inhibition effects. This work presents a new transdermal treatment nanoplatform for dual-modal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy of superficial tumors, with efficient tumor eradication and low systemic toxicity thus offering strong potential for clinical adoption.
双癸基二甲基溴化铵是一种阳离子表面活性剂,分子结构中含有两个癸基、两个甲基和一个溴离子。这种结构赋予它良好的表面活性,能有效降低液体表面张力。具备良好的乳化能力,可使油和水形成稳定乳液,在乳液聚合等行业有用途,它化学性质相对稳定。该文献开发了一种纳米平台(+)T-SiDs,基于超顺磁氧化铁核,表面修饰的阳离子脂质,经皮增强肽TD,和1,1‘-二十八烷基-3,3,3’,3‘-四甲基线三溴氰碘化物(DiR),并装载阿霉素。过程如下:
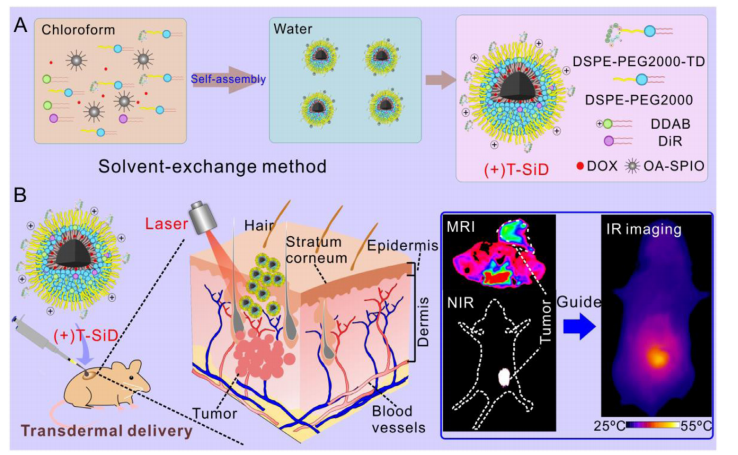
图:(+)T-SiDs的合成过程及作用机制
(+)T-SiDs的合成
采用改性法合成了(+)T-SiD纳米颗粒。简单地说,将SPIO、DiR、DOX、DSPE-PEG2000-TD、DSPE-PEG2000和DDAB按照一定质量比溶解在氯仿中。然后,逐渐向混合物中加入四体积的乙二醇。在用旋转蒸发器蒸发氯仿完全后,用超滤离心机用水取代乙二醇。然后,将溶液超声处理。最后,将溶液离心,丢弃沉淀物以去除大的聚集体。TSiDs、(+)T-SDs、(+)SiDs和(+)T-Sis分别采用相同的方法合成,不含DDAB、DiR、TD和DOX。
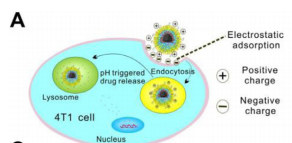
图:细胞摄取(+)t-sid的摄取和DOX的ph响应释放示意图
结论:DSPE-PEG2000-NHS和双癸基二甲基溴化铵(DDAB)参与制备的(+)T-SiDs具有良好的稳定性、细胞吸收、pH/光热反应性药物释放和较高的光热转化效率(47.45%)。TD功能化增强了(+)T-SiDs的经皮传递。体内MR/NIR成像显示,(+)t-sid在对tumor部位的定位方面具有较高的透皮效率和特异性。

 2025-04-03 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-04-03 作者:ZJ 来源:

