文献:Choice of Nanovaccine Delivery Mode Has Profound Impacts on the Intralymph Node Spatiotemporal Distribution and Immunotherapy Efficacy
文献链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202001108
作者:Jianghua Wang, Shuang Wang, Tong Ye, Feng Li, Xiaoyong Gao, Yan Wang, Peng Ye, Shuang Qing, Changlong Wang, Hua Yue, Jie Wu, Wei Wei,and Guanghui Ma
相关产品:
Cholesterol 胆固醇
原文摘要:Nanovaccines have attracted booming interests in vaccinology studies, but the profound impacts of their delivery mode on immune response remain unrealized. Herein, immunostimulatory CpG-modified tumor-derived nanovesicles (CNVs) are used as a nanovaccine testbed to initially evaluate the impacts of three distinct delivery modes, including mono-pulse CNVs, staggered-pulse CNVs, and gel-confined CNVs. Fundamentally, delivery mode has enormous impacts on the immunomodulatory effects, altering the spatiotemporal distribution of nanovaccine residence and dendritic cell–T cell interaction in lymph nodes, and finally affecting subsequent T cell-mediated immune performance. As a result, the gel-confined delivery mode offers the best therapeutic performance in multiple tumor models. When extending evaluation to examine how the various delivery modes impact the performance of liposome-based nanovaccines, similar trends in intralymph node distribution and antitumor effect are observed. This work provides a strong empirical foundation that nanovaccine researchers should position delivery mode near the top of their considerations for the experimental design, which should speed up nanovaccine development and facilitate efficient selection of appropriate delivery modes in the clinic.
DSPE-PEG2000二硬脂酰基磷脂酰乙醇胺-聚乙二醇2000,是一种基于脂质的分子,由二硬脂酸-sn-甘油-3-磷酸乙醇胺(DSPE)的磷脂和一个平均分子量为2000的聚乙二醇(PEG)链组成。胆固醇是构成细胞膜的重要成分,对调节膜的流动性、加强膜的稳定性有重要作用。基于这些材料饿性质该文献通过免疫刺激cpg修饰的CNVs被用作纳米Blood vessels试验台,以初步评估三种不同传递方式的影响,包括单脉冲CNVs、交错脉冲CNVs和凝胶限制CNVs。从根本上说,传递方式对免疫调节作用有巨大的影响,改变纳米细胞和Lymph 结树突状细胞-T细胞相互作用的时空分布,最终影响随后的T细胞介导的免疫性能。今天制备如下:
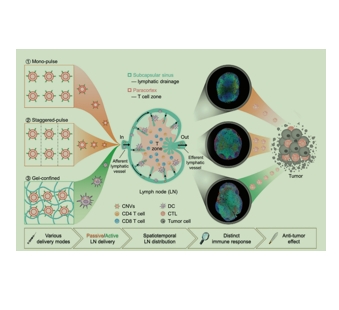
图为:通过不同的传递方式对tumor免疫Treatment 中纳米疫苗Lymph 结内分布的时空调节。
DSPE-PEG2000和Cholesterol在CNVs和脂纳米疫苗M/S@Lipo制备中的应用:
采用典型的膜分散法合成了M/S@Lipo。将DOPC、DSPE-PEG2000、胆固醇和MPLA混合在氯仿/甲醇溶液中。之后,将混合物在旋转蒸发器上蒸发成一层薄膜。将制备的薄膜在真空下进一步干燥过夜,完全去除溶剂,并在含有辛甲克肽的PBS溶液中再水合,超声处理。最终,通过聚碳酸酯膜挤压,形成均匀的M/S@Lipo。对于荧光M/S@Lipo的制备,在蒸发过程前,将荧光染料DiD加入到氯仿/甲醇混合物中。通过上述超滤程序去除多余的含量和染料。同样,用DOPC、DSPE-PEG2000和胆固醇按照上述工艺制备空白脂肪。采用反相高效液相色谱法(RP-HPLC)检测MPLA和辛甲克肽的含量。
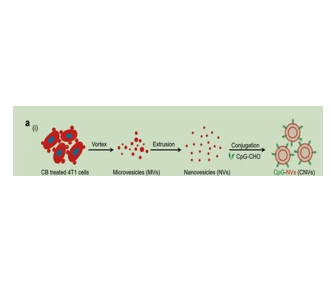
图为:cnv的制备原理图
DSPE-PEG2000 中的聚乙二醇(PEG)部分具有良好的亲水性,在制备脂纳米疫苗 M/S@Lipo 过程中,其能够在脂质纳米颗粒表面形成一层水化层。这层水化层可以阻止纳米颗粒之间的聚集,提高纳米颗粒的稳定性,防止其在储存和运输过程中发生沉淀或变质。在涉及到CNVs的应用中,稳定的纳米颗粒可以更好地保持化合物的活性,确保在到达病变部位时能够发挥有效的作用。胆固醇是脂质双分子层的重要组成部分,在制备脂纳米疫苗 M/S@Lipo 时,适量的胆固醇可以调节脂质膜的流动性。合适的膜流动性对于包裹和保护化合物或疫苗成分至关重要,它可以确保纳米颗粒在制备过程中保持稳定的结构,防止化合物泄漏。在 CNVs 中,调节膜流动性可以影响化合物从纳米颗粒中的释放速率,实现化合物的控释,提高效果。

 2025-03-27 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-03-27 作者:lkr 来源:

