文献:
Hyaluronic acid extracellularly inhibits ferroptosis via cell-surface receptors in acute traumatic brain injury,Nano Today,Volume 46,2022,
文献链接:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363887606_Hyaluronic_acid_extracellularly_inhibits_ferroptosis_via_cell-surface_receptors_in_acute_traumatic_brain_injury
作者:
Zhiqiang Liu, Xiaowen Xing, Pengchong Zhu, Cui Wang, Mengwen Song, Lei Zhang, Xiaoming Zhu, Bin Ning, Yuming Fu, Zengqiang Yuan
相关产品:
原文摘要:
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an important cause of death and disability in young people worldwide without effective treatment. Ferroptosis was recently reported to be related to TBI and provided a potential target for developing new therapeutic strategies, but how it influenced TBI and the underlying mechanism were still unclear. Here, with multimodality of methods, ferroptosis was demonstrated to mainly occur in acute TBI. Further, we found that hyaluronic acid (HA), a natural extracellular matrix (ECM) material, could markedly and specifically inhibit ferroptosis in cells and TBI mice. Preblocking the HA-receptor interaction or CRISPR/Cas9-based gene deletion of HA putative receptors neurocan (NCN) and CD44 abolished the anti-ferroptosis effect of HA. Importantly, it was demonstrated that CD44 was significantly up regulated by tens of folds in the focus area of TBI. Through intravenous injection of Cy5-HA nanoconjugates, it was shown that HA could effectively bind to the TBI site like a targeting nanodrug and then, significantly reduced brain damage and behavioral defects. Collectively, we demonstrated HA as the natural anti-ferroptosis material which acted through receptor-mediated intrinsic signaling pathways, and developed a new therapeutic avenue for acute TBI treatment. Moreover, the new function of HA revealed in the study confirmed the existence of extracellular regulation of ferroptosis, and would largely promote the development of novel nanomaterials or nanodrugs for ferroptosis-related tissue injuries.
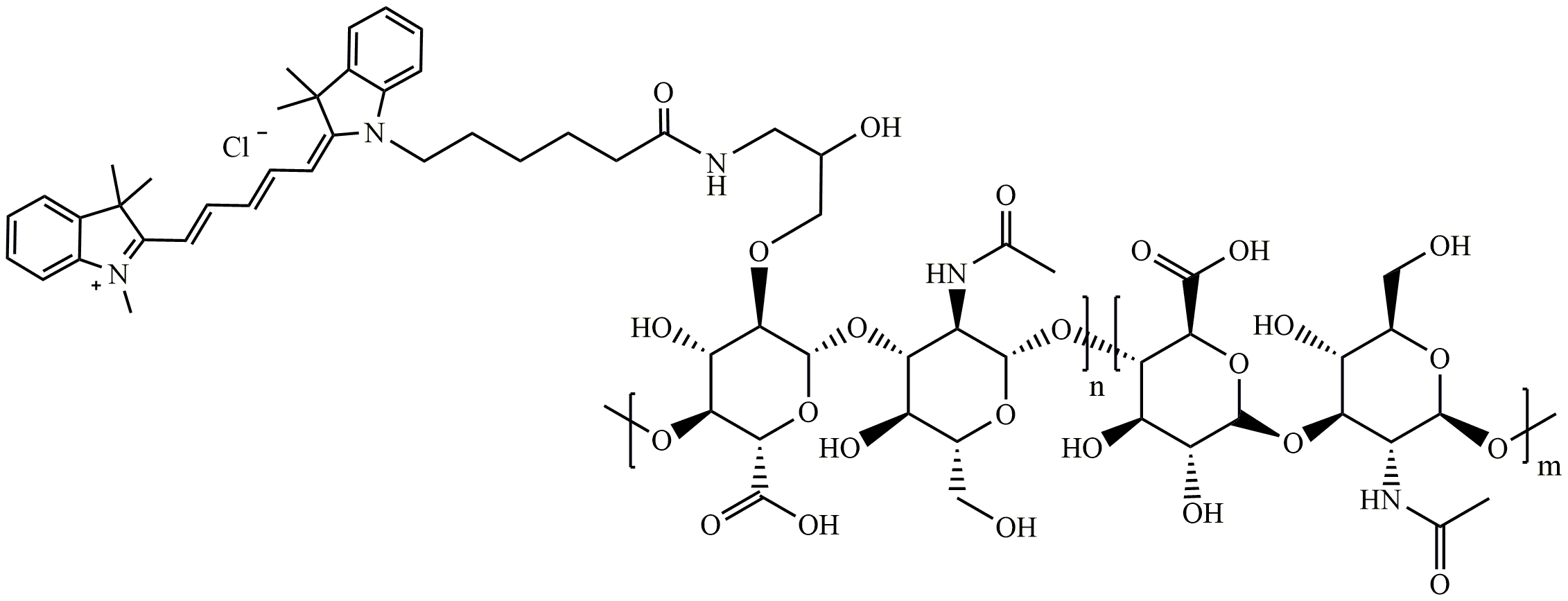
图为:Cy5-HA结构式
透明质酸(HA),一种天然的细胞外基质(ECM)材料,可以特异性地抑制细胞和TBI小鼠的脱铁性。预先阻断HA受体相互作用或基于CRISPR/Cas9的HA推定受体神经干(NCN)和CD44的基因缺失消除了HA的抗脱铁作用。
研究表明CD44在TBI的焦点区域上调了几十倍。通过静脉注射Cy5-HA纳米偶联物,研究表明HA可以像靶向纳米药物一样与TBI位点结合,从而减少脑损伤和行为缺陷。总之HA是一种通过受体介导的内在信号通路发挥作用的天然抗脱铁性材料,并为急性TBI的Treatment开辟了一条新的Treatment途径。此外,研究中揭示的HA的新功能证实了脱铁症细胞外调节的存在,并将在很大程度上促进新型纳米材料或纳米药物的开发。

 2025-03-18 作者:wff 来源:
2025-03-18 作者:wff 来源:

