文献:Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy of Dual Drug-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated by pH-Responsive Folic Acid and Human-Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide dNP2
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33921919/
作者:Zhe Ma, Jiaxin Pi, Ying Zhang, Huan Qin, Bing Zhang, Nan Li, Zheng Li,Zhidong Liu
相关产品:
原文摘要:The poor ability of recognition and penetration of chemotherapeutic agents to tumor cells are still great challenges for targeted breast cancer treatment. Herein, we established a tumor-targeted nanostructured lipid carrier encapsulating gambogic acid (GA) and paclitaxel (PTX), which was co-modified with acid-cleavable folic acid (cFA) and a human-derived cell penetrating peptide dNP2 (CKIKKVKKKGRKKIKKVKKKGRK). The multi-functional nano-platform exhibited an enhanced targeting and penetrability to tumor tissues, which was accomplished by the combined action of cFA and dNP2. After intravenous injection, firstly, cFA could actively target the breast cancer tissues by the selective recognition of folate receptor (FR); then, upon arrival at the tumor microenvironment, the acid-cleavable FA and dNP2 dual modified nanostructured lipid carrier (cFA/dNP2-GA/PTXNLC) exhibited sensitive cleavage of folic acid (FA), which could reduce the hindrance effect of FA to maximize the dNP2 cell-penetrating properties. The effect of different modification on cellular uptake, in vivo bio-distribution, and anticancer activity of NLCs proved our hypothesis that compared with NLCs modified by non-cleavable FA or a single ligand, cFA/dNP2-GA/PTX-NLC displayed more efficient intracellular delivery, stronger targeting ability in vivo, improved cytotoxicity on 4T1 cells, and produced the better therapeutic efficacy of GA and PTX. The strategy affords a feasible way to overcome the poor recognition and permeability of medicines in cancer treatment.
叶酸(Folic Acid,FA)是一种水溶性维生素,也称为维生素 B9。叶酸在细胞分裂和生长过程中起着重要的作用。它参与 DNA 和 RNA 的合成,对于细胞的正常生长和分裂至关重要。叶酸还参与氨基酸代谢、血红蛋白合成等生理过程。NLC是从固体脂质纳米粒(SLN)发展而来的纳米粒传输系统。它是固体和液体脂质的混合物经表面活性剂乳化后形成的纳米粒,具有更好的胶体稳定性和持续的化合物释放行为。NLC结合了脂基纳米载体(如脂质体、纳米乳剂)高生物利用度和高生物相容性等优势,并且相较于其他脂基胶体载体,其刚性形态、高物理稳定性、抗载荷降解等优点确保了更高的安全性。叶酸在许多方面有着应用,例如引用的此篇文献在纳米结构脂质载体NLC的制备过程中。具体制备过程如下:
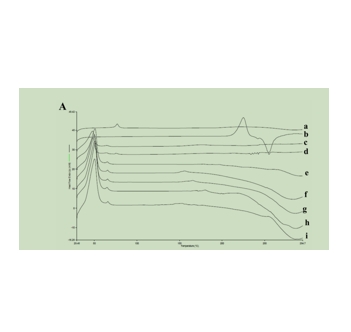
图为:不同配方的差示扫描量热法
叶酸FA在纳米结构脂质载体NLC制备中的应用:
乳化和溶剂蒸发法用于制备NLCS。为了获得由FA、dNP2、FA/dNP2和cFA/dNP2等不同材料修饰的NLCS,用等量的配方材料替换大豆卵磷脂,配方材料的量确定。根据研究结果,GA和PTX(GA和PTX被包封在NLCS中,荧光染料Cou-6和DiR被添加到油相中,用于制备GA/PTX-NLC、Cou-6-NLC或DiR-NLC。
FA在体内生物分布研究中的应用:
以DiR为荧光探针,通过体内成像系统(IVIS)研究了含4T1细胞的BALB/c裸鼠中不同NLC制剂的tumor靶向性和动态分布。简单地说,雌性BALB/c裸鼠皮下注射4T1细胞悬液,将小鼠随机分为7组(a:生理盐水、b:DiR-Sol、c:DiR-NLC、d:dNP2-DiR-NLC、e: FA-DiR-NLC、f: FA/dNP2-DiR-6-NLC、g:cFA/dNP2-DiR-NLC)。给药后,用水合氯醛麻醉小鼠,置于IVIS中观察各器官的荧光强度。一天后,每组die小鼠,采集器官,然后测定其荧光强度。
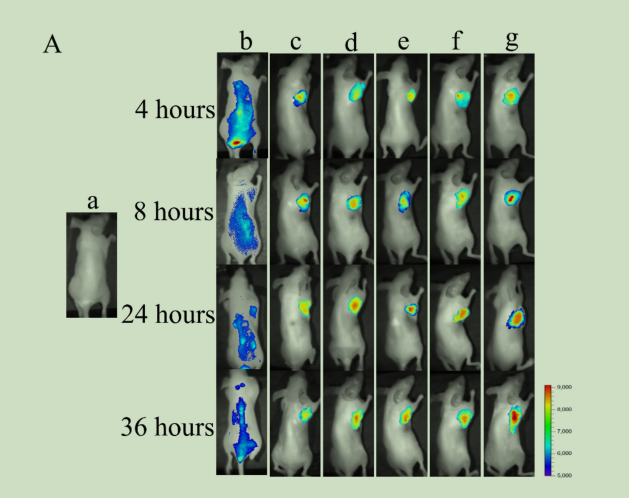
图为:改良DiR-NLC在荷瘤小鼠中的生物分布研究
结论:FA(叶酸)在NLC(纳米结构脂质载体)制备中的应用主要体现在提高化合物的靶向性和生物利用度方面。FA在NLC制备中的一个应用优势是其能够提高化合物的靶向性。由于多种tumor细胞的表面存在过量的叶酸受体表达,通过将FA连接到NLC表面,可以利用这些受体介导的内吞作用,使化合物更准确地靶向到tumor细胞。这种靶向性不仅提高了化合物的效果,还减少了化合物对正常组织的损伤。FA修饰的NLC能够提高化合物的生物利用度。由于FA的靶向作用,化合物能够更多地蓄积在tumor部位,从而提高了局部化合物浓度。

 2025-02-17 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-17 作者:lkr 来源:

