文献:
Optical Tracking of Phagocytosis with an Activatable Profluorophore Metabolically Incorporated into Bacterial Peptidoglycan
文献链接:
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01633
作者:
Yunpeng Tian†, Mingzu Yu†, Zhu Li†, Jiahuai Han‡, Liu Yang*†, and Shoufa Han*†
相关产品:
原文摘要:
Phagocytosis is critical for immunity against pathogens. Prior imaging using dye-labeled synthetic beads or green fluorescent protein-expressing bacteria is limited by “always-on” signals which compromise discerning phagocytosed particles from adherent particles. Targeting cellular internalization of pathogens into acidic phagolysosomes, we herein report “turn-on” fluorescence imaging of phagocytosis with viable bacteria featuring peptidoglycans covalently modified with rhodamine-lactam responsive to acidic pH. Culturing of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) with d-lysine conjugated rhodamine-lactam and fluorescein isocyanate (FITC) leads to efficient metabolic incorporation of FITC and rhodamine-lactam into bacterial peptidoglycan. E. coli and S. aureus become red-emissive upon phagocytosis into Raw 264.7 macrophages. With FITC as the reference signal, the mono- and dual-color emission allow efficient in situ distinction of ingested bacteria from extracellular bacteria. Given the ease of optical peptidoglycan labeling, the prevalence of microbial peptidoglycan and preservation of microbial surface landscape, this approach would be of use for investigation on microbial pathogenesis and high-throughput screening of immunomodulators of phagocytosis.
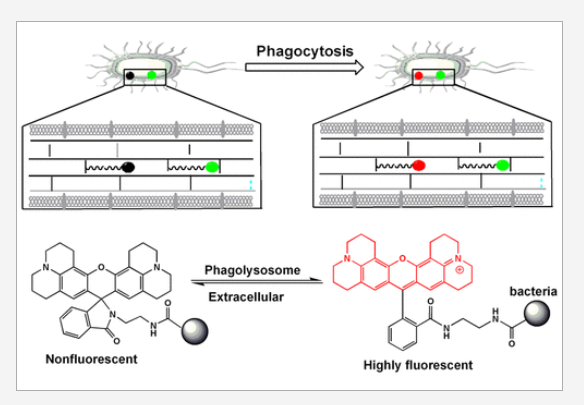
使用染料标记的合成珠或绿色荧光蛋白表达Bacteria的成像受到“常亮”信号的限制,该信号损害了从粘附颗粒中识别吞噬颗粒的能力。针对病原体在酸性吞噬多胞体中的细胞内化,活Bacteria吞噬作用的“开启”荧光成像,其特征是用罗丹明-内酰胺共价修饰的肽聚糖对酸性pH响应。用d-赖氨酸缀合的罗丹明内酰胺和异氰酸荧光素(FITC)培养大肠杆菌(E.coli)和金黄色葡萄球菌(S.aureus)导致FITC和罗丹明内酰胺有效地代谢结合到Bacteria肽聚糖中。大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌在吞噬成Raw 264.7巨噬细胞时变成红色发射。
以FITC为参考信号,单色和双色发射可以有效地原位区分摄入的Bacteria和细胞外Bacteria。考虑到光学肽聚糖标记的容易性、微生物肽聚糖的普遍性和微生物表面景观的保存,这种方法将用于研究微生物发病机制和高通量筛选吞噬作用的免疫调节剂。

 2024-11-18 作者:wff 来源:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01633
2024-11-18 作者:wff 来源:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01633

