文献:Cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-modified red blood cells for drug delivery: synthesis and in vitro evaluation
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=11480m90j91t0r70rq0r0rc06r111936&site=xueshu_se
作者:Chen Wang , Min Wang , Yan Zhang, Hongxin Jia, Binbin Chen
相关产品:
avidin 亲和素
DSPE-PEG3400-biotin 磷脂-聚乙二醇3400-生物素
原文摘要:Red blood cell (RBC)was an excellent choice for cell preparation researchbecause of their biocompatibility, high drug loading, and long half-life. In this studydoxorubicin (DOX)was encapsulated with red blood cells as the carrier. Thebiotin-avidin system binding principle was used to modify biotinylated cyclicarginine-glycine-aspartic acid (cRGD)onto red blood cell surfaces for accuratetargeting, high drug loading, and sustained drug release. The red blood cell drugdelivery system (DDS) was characterized, and the concentration of surface sulfur inthe energy spectrum was 6.330%. The physical and chemical properties of red bloodcell DDS were as follows: drug content, 0.857 mg/mL; particle size, 3,339 nm,potential value, -12.5 mV; and cumulative release rate, 81.35%. There was nosignificant change in red blood cell morphology for up to seven days. The results ofthe targeting and cytotoxicity studies of red blood cell DDS showed that many redblood cells covered the surfaces of U25l cells, and the fluorescence intensity washigher than that of MCF-7 cells. The IC50 value of unmodified drug-loaded red bloodcells was 2.5 times higher than that of targeted modifed drug-loaded red blood cells.indicating that the targeting of cancer cells produced satisfactory inhibition. Thisstudy confirms that the red blood cell DDS has the characteristics of accuratetargeting, high drug loading, and slow drug release, which increases its likelihood ofbecoming a clinical cancer treatment in the future.
磷脂-聚乙二醇3400-生物素从结构上看,磷脂部分具有疏水性,能与脂质类物质很好地融合,为整个分子提供了与细胞膜等脂质环境相互作用的基础。聚乙二醇3400(PEG3400)具有亲水性,赋予材料在水相中的溶解性和稳定性。它可以减少材料在体内的非特异性吸附,延长其在体内循环中的停留时间。生物素与亲和素之间具有极高的亲和力。这种材料可用于构建化合物递送系统,将化合物包裹在其形成的载体结构内。其生物素部分可通过与亲和素或链霉亲和素的特异性结合,实现对化合物载体的进一步修饰、靶向定位等功能,例如将化合物准确递送至表达亲和素相关受体的细胞或组织。该文献研究以阿霉素(DOX)为载体。利用生物素-亲和素系统结合原理,将生物素化的环精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸(cRGD)修饰到红细胞表面,以实现准确的靶向、高化合物载量和持续的化合物释放。制备过程如下:
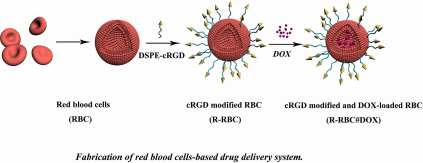
图:基于红细胞的化合物传递系统示意图
cRGD修饰的红细胞(R-RBC)的制备
将 DPSE-peg3400-生物素和红细胞悬浮于 PBS中,摇匀。离心,将沉淀物(b-RBC)和亲和素悬浮于PBS中,摇匀,将亲和素与红细胞表面(A-b-RBC)上的生物素连接起来。根据上述方法,加入cyclo[RGDfK(生物素)],获得经cRGD(R-RBC)表面修饰的红细胞。
制备装载DOX的R-RBC (R-RBC#DOX)
将DOX与红细胞悬液混合,在低渗缓冲液(分子量截止=3500)中透析。将包封DOX的红细胞转移到高渗缓冲液中,然后离心去除未包封的DOX。该化合物被通过红细胞的“打开和关闭”膜包裹在红细胞中。
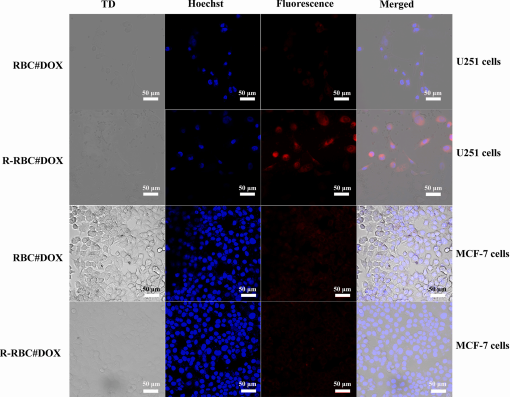
图:经RBC#DOX和R-RBC#DOX处理后,U251细胞和MCF-7细胞的细胞摄取
结论:DPSE-peg3400-生物素参与制备了一种基于红细胞的DDS。对红细胞表面进行修饰,将DOX包裹在红细胞中,具有慢释、高化合物载量和准确靶向特性,验证了DDS的物理化学性质、靶向特性,利用生物素亲和素反应对红细胞表面进行修饰。载药前后红细胞的结构、大小和潜在特征均无明显变化。细胞DDS也表现出7天的缓释和良好稳定性的特性,具有良好的整合素avβ靶向特性。

 2025-02-17 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-17 作者:ZJ 来源:

