文献:A non-invasive nanoparticles for multimodal imaging of ischemic myocardium in rats
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33752679/
作者:Xiajing Chen, Yanan Zhang, Hui Zhang, Liang Zhang, Lingjuan Liu, Yang Cao, Haitao Ran,Jie Tian
相关产品:
IMTP
DSPE-PEG2000-IMTP 磷脂-聚乙二醇 2000-IMTP
原文摘要:
Background: Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and imposes a serious economic load. Thus, it is crucial to perform a timely and accurate diagnosis and monitoring in the early stage of myocardial ischemia. Currently, nanoparticles (NPs) have emerged as promising tools for multimodal imaging, because of their advantages of non-invasion, high-safety, and real-time dynamic imaging, providing valuable information for the diagnosis of heart diseases.
Results: In this study, we prepared a targeted nanoprobe (termed IMTP-Fe3O4-PFH NPs) with enhanced ultrasound (US), photoacoustic (PA), and magnetic resonance (MR) performance for direct and non-invasive visual imaging of ischemic myocardium in a rat model. This successfully designed nanoprobe had excellent properties such as nanoscale size, good stability, phase transformation by acoustic droplet vaporization (ADV), and favorable safety profle. Besides, it realized obvious targeting performance toward hypoxia-injured cells as well as model rat hearts. After injection of NPs through the tail vein of model rats, in vivo imaging results showed a signifcantly enhanced US/PA/MR signal, well indicating the remarkable feasibility of nanoprobe to distinguish the ischemic myocardium.
Conclusions: IMTP-Fe3O4-PFH NPs may be a promising nanoplatform for early detection of ischemic myocardium and targeted treatment under visualization for the future.
IMTP是通过体内Bacteriophage 显示筛选的环9氨基酸序列(CSTSMLKAC)。它在纳米粒子体系中发挥着重要的作用。该肽可以优先进入Ischemic myocardium中的musculus 细胞,作为活性靶向标记物IMTP已被偶联在NPs表面以进行主动靶向。IMTP-Fe₃O₄-PFH NPs 是一种具有特定组成和潜在应用价值的纳米粒子体系。结合了 IMTP 的特定功能、Fe₃O₄的磁性和 PFH 的相变特性,使得这种纳米粒子体系具有多种潜在应用。IMTP在许多方面有应用,例如这篇文献就介绍了在IMTP-Fe3O4-PFH NPs制备过程中。具体制备过程如下:
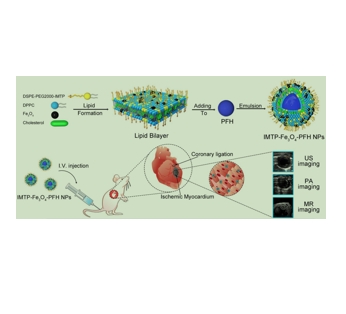
图为:IMTP-Fe3O4-PFH NPs的合成程序
IMTP在IMTP-Fe3O4-PFH NPs制备过程中的应用:
IMTP的引入会对Fe₃O₄纳米颗粒的形貌和尺寸产生影响,从而调控纳米颗粒的物理和化学性质。通过调节IMTP的修饰程度和方式,可以制备出具有不同形貌和尺寸的IMTP-Fe₃O₄-PFH NPs。IMTP的修饰会改变Fe₃O₄纳米颗粒的表面性质,从而影响制备过程中的一些关键步骤。通过优化IMTP的修饰条件和方式,进一步提高IMTP-Fe₃O₄-PFH NPs的制备效率和产品质量。IMTP作为一种生物相容性良好的材料,被用于修饰Fe₃O₄纳米颗粒的表面,以减少纳米颗粒在生物体内的有害性反应,并增加其在生物环境中的稳定性。

图为:IMTP-PFH NPs和IMTP-Fe3O4-PFH NPs的照片
结论:IMTP 可能具有特定的结构或化学基团,能够与特定的生物分子、细胞或组织相互作用,从而使制备出的纳米粒子具有靶向性。例如,IMTP 可能能够识别并结合tumor细胞表面的特定受体,使得纳米粒子能够特异性地聚集在tumor部位,提高效果并减少对正常组织的副作用。IMTP 可能参与纳米粒子的合成过程,与其他成分发生化学反应,形成特定的结构或化学键。例如,IMTP 可能与 Fe₃O₄(四氧化三铁)和 PFH(全氟己烷)等成分通过共价键或非共价键结合,形成稳定的纳米粒子结构。通过IMTP的修饰,可以改善Fe₃O₄纳米颗粒在水溶液或其他溶剂中的分散性,防止纳米颗粒的团聚和沉淀,从而有利于其在后续应用中的均匀分布和性能发挥。

 2025-02-14 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-14 作者:lkr 来源:

