文献:A cancer-specific activatable theranostic nanodrug for enhanced therapeutic efficacy via amplification of oxidative stress
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31903126/
作者:Xie-an Yu, Mi Lu, Yingping Luo, Yiting Hu, Ying Zhang, Zhiming Xu, Shuaishuai Gong, Yunhao Wu, Xiao-Nan Ma, Bo-Yang Yu, Jiangwei Tian
相关产品:DSPE-PEG2000-Tf 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-转铁蛋白
原文摘要:Rationale: Despite considerable advances, the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated cancer treatment suffers from the problems of up-regulation of adaptive antioxidants in cancer cells as well as side effects to normal cells. Therefore, development of a new generation of cancer-specific nanomedicine capable of amplifying oxidative stress would be of great interest for accurate and effective cancer treatment.
Methods: Herein, transferrin (Tf)-decorated, dihydroartemisinin (DHA), L-buthionine-sulfoximine
(BSO), and CellROX-loaded liposomal nanoparticles (Tf-DBC NPs) were developed for precise cancer theranositcs. Tf-DBC NPs could specifically recognize cancer cells via Tf-Tf receptor binding and be uptaken into the lysosomes of cancer cells, where Tf-DBC NPs were activated to release Fe(II), DHA, and BSO. ROS was generated by DHA in the presence of Fe(II), and GSH was depleted by BSO to disrupt the redox balance in cancer cells. Furthermore, CellROX, as a fluorescent probe
for imaging of intracellular oxidative stress, was used to monitor the therapeutic efficacy.
Results: The integration of Tf, DHA, and BSO into the acidic pH-responsive liposomes selectively and effectively killed cancer cells and prevented the oxidative injury to normal cells. The high oxidative state was visualized at the tumor site and the amplification of oxidative stress enabled tumor eradication by Tf-DBC NPs, demonstrating the successful implementation of this novel strategy in vivo.
Conclusion: Our study provides a new paradigm for the design of ROS-mediated therapeutics and offers a promising perspective for precise cancer treatment.
DSPE-PEG2000-Tf是由磷脂分子(DSPE)、聚乙二醇(PEG)和转铁蛋白(Tf)通过特定化学键连接而成的化合物。通过转铁蛋白(Tf)的靶向作用,DSPE-PEG2000-Tf能够引导Tf-DBC NPs特异性地识别并结合cancer细胞表面的转铁蛋白受体,从而实现化合物的靶向递送,提高化合物的效果并减少副作用。在此,转铁蛋白(Tf)修饰、双氢青蒿素(DHA)、l-丁硫氨酸亚胺(BSO)和cellrox负载脂质体纳米颗粒(Tf-DBC NPs)。Tf-DBC NPs可以通过Tf-Tf受体结合来特异性识别cancer细胞,并被摄取到cancer细胞的溶酶体中,在那里Tf-DBC NPs被激活,释放Fe(II)、DHA和BSO。
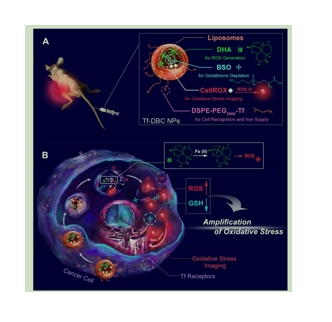
图为:Tf-DBC NPs的(A)结构和(B)功能示意图
DSPE-PEG2000-Tf在Tf-DBC NPs合成中的应用:
采用薄膜水化法制备了Tf-DBC NPs。使用DSPE-PEG2000-Tf、DOPE和CHEMS的混合物脂质体配方。将 DHA和CellROX溶解在由氯仿:甲醇组成的溶剂中。溶液蒸发干燥几分钟,直到在底部形成脂质薄膜。随后,用含有 BSO的无菌磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)重新溶解瓶中的脂质膜。为了制备分散良好的NPs,溶液经过超声处理,用聚碳酸酯膜过滤。
DSPE-PEG2000-Tf在Tf-DBC NPs表征中的应用:
选择脂质体作为纳米载体,利用DSPE-PEG2000-Tf、DOPE和CHEMS进行组装。在脂膜形成过程中加入了疏水的DHA和CellROX,而亲水的BSO被包裹在水核中。采用薄膜水化法制备共载脂质体纳米颗粒(Tf-DBC NPs),然后根据形貌、颗粒径和表面电荷进行了表征。通过TEM和DLS分析可以明显看出,Tf-DBC NPs呈纳米结构的球形,分散均匀。Tf-DBC NPs大小的轻微增加可能归因于脂质体上的Tf装饰。此外,与空白脂质体相比,用Tf修饰脂质体后,有一个强烈的特征吸收峰,表明Tf在脂质双分子层上的嫁接成功。DBC NPs和Tf-DBC NPs的zeta电位表明内埋的Tf不影响脂质体的稳定性。Tf-DBC NPs和DBC NPs的PDI值也几乎相同。
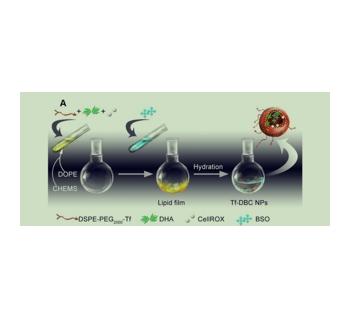
图为:Tf-DBC NPs的合成
结论:DSPE-PEG2000-Tf作为纳米载体的组成部分,其PEG链段能够在脂质体表面形成一层水化膜,有效减少脂质体与血浆中蛋白、酶等成分的结合,从而提高脂质体纳米粒子在体内中的稳定性和循环时间。在Tf-DBC NPs中,DSPE-PEG2000-Tf作为载体,能够同时装载双氢青蒿素(DHA)、L-丁硫氨酸-亚砜亚胺(BSO)和CellROX等多种活性成分。这些成分在cancer细胞内部能够发挥协同作用,共同破坏cancer细胞的氧化还原平衡。DSPE-PEG2000-Tf的载体作用使得这些活性成分能够更有效地到达cancer细胞内部,从而提高了效果。

 2025-02-14 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-14 作者:lkr 来源:

