文献:Cuboidal tethered cyclodextrin frameworks tailored for hemostasis and injured vessel targeting
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31131049/
作者:Yaping He, Jian Xu, Xian Sun, Xiaohong Ren, Abi Maharjan, Peter York, Yong Su, Haiyan Li, Jiwen Zhang
相关产品:Cy5 五甲川花菁染料
原文摘要:Rationale: Targeted delivery of therapeutic drugs or imaging agents to injured blood vessels via nanocarriers is likely to be dependent on the particle shape, yet cubic nanoparticle carriers have not been reported for vascular targeting. Here, we demonstrate that cuboidal cyclodextrin frameworks possess superior hemostasis effect and injured vessels targeting compared with spherical counterpart.
Methods: Cuboidal and biocompatible γ-cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks (CD-MOFs) are synthesized, tethered via crosslinking and surface modification with GRGDS peptide (GS5-MOFs). The specific interactions of cubic GS5-MOF nanoparticles with activated platelets were investigated by in vitro platelet aggregation assay and atomic force microscopy measurements (AFM). The hemostatic capacity and injured vessel targeting efficacy were evaluated in vivo.
Results: Cuboidal GS5-MOF nanoparticles exhibit enhanced adhesion and aggregation with activated platelets in vitro under static condition and a physiologically relevant flow environment. The cubic GS5-MOF nanoparticles show efficient hemostatic effects with bleeding time and blood loss decrease of 90% and strong injured vessel targeting in vivo, markedly superior to spherical γ-CD nanosponges with the same chemical composition.
Conclusions: These results clearly highlight the contribution of the cuboidal shape of GS5-MOFs to the enhanced aggregation of activated platelets and high targeting to damaged vessels. The cuboidal nanoparticle system provides an innovative delivery platform for the treatment and diagnosis of vascular diseases.
Cy5作为一种近红外荧光染料,具有强烈的荧光特性,其荧光波长通常在650nm左右。这一特性使得Cy5能够在低背景干扰下提供高灵敏度的检测,适用于细胞成像研究。当Cy5与RGD结合形成Cy5-RGD复合物时,该复合物能够利用RGD的生物活性,特异性地与细胞表面的整合素受体结合。这种结合不仅保留了RGD的生物功能,还赋予了复合物荧光标记的能力,能够通过荧光显微镜观察细胞黏附、信号转导和细胞迁移等生物学过程,从而更深入地了解这些过程的分子机制。
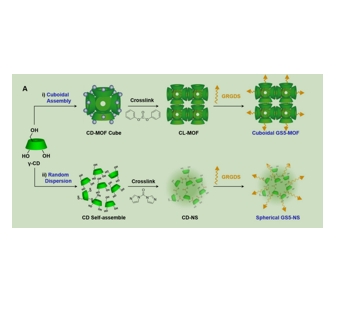
图为:将GRGDS偶联在CL-MOF表面,得到GS5-MOF纳米颗粒
Cy5在RGD生物功能化中的应用:
GRGDS肽与CL-MOFs和CD-NS表面的稳定连接对于blood cells的强粘附和聚集至关重要。为了提供稳定的键,GRGDS肽通过CL-MOFs和CD-NS的表面羟基与GRGDS的c端反应,通过稳定的共价酯键共价连接到CL-MOF和CD-NS纳米颗粒上。CL-MOFs(或CD-NS)和GRGDS添加到圆底瓶DMF溶剂,和简单的化学反应进行加热、搅拌EDC和DMAP催化剂GRGDS肽表面CL-MOF纳米颗粒(或CD-NS)。然后用甲醇和水洗涤两次,用冻干干燥。GRGDS修饰的CL-MOF和CD-NS纳米颗粒分别命名为GS5-MOF和GS5-NS。Cy5与Cy5中的游离羟基(-羧基)反应,对CL-MOF、GS5-NS和GS5-MOF纳米颗粒进行荧光标记。即,将Cy5和CL-MOF(GS5-NS或GS5-MOF)纳米颗粒放在DMF中,在黑暗中搅拌。
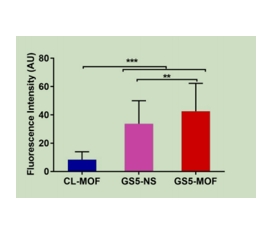
图为:cy5标记的CL-MOF、GS5-NS和GS5-MOF纳米颗粒相互作用的代表性荧光显微镜图像
结论:由于RGD能够特异性地与tumor细胞或新生vessel表达的整合素结合,因此Cy5-RGD可以作为一种具有荧光特性的生物分子,用于筛选和开发针对与细胞黏附、信号转导和细胞迁移相关的化合物。通过监测Cy5-RGD与细胞或组织的结合情况,可以评估化合物的效果和安全性。RGD作为一种常见的tumor主动靶向性多肽,可以直接作用于tumor靶点,形成主动靶向性效果。当Cy5与RGD结合后,Cy5-RGD复合物能够利用RGD的靶向性,将化合物或其他物质递送到tumor组织,从而提高针对性和有效性。

 2025-02-14 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-14 作者:lkr 来源:

