文献:Transferrin-Pep63-liposomes accelerate the clearance of Aβ and rescue impaired synaptic plasticity in early Alzheimer’s disease models
文献链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41420-021-00639-1
作者:Xiu Yang , Xu Li, Le Liu, Yuan-Hao Chen , Yue You, Yin Gao , Yue-Ying Liu, Li Yang, Kun Tong , Di-Shi Chen , Jing-Ru Hao , Nan Sun , Zi-Ming Zhao and Can Gao
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG2000-Cy5.5 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-Cy5.5菁染料
DMPA 二肉豆蔻酰磷脂酸
原文摘要:Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by aberrant accumulation of extracellular β-amyloid (Aβ) peptides in the brain. Soluble Aβ oligomers are thought to be the most neurotoxic species and are correlated with cognitive dysfunction in early AD. However, there
is still no effective treatment so far. We determined that Pep63, a small peptide, had a neuroprotective effect on synaptic plasticity and memory in our previous study. Here, we developed novel and multifunctional liposomes targeting both Aβ oligomers and fibrils based on a liposome delivery system. Transferrin-Pep63-liposomes (Tf-Pep63-Lip), possessing the ability
for blood-brain barrier targeting, were also incorporated with phosphatidic acid (PA) and loaded with neuroprotective Pep63. We discovered that administration of Tf-Pep63-Lip could significantly reduce the Aβ burden in the hippocampus, and improve cognitive deficits in 6-
month-old APP/PS1 mice in the Morris-Water maze task and fear-conditioning test with the combined effects of PA and Pep63. TfPep63-Lip could capture Aβ oligomers or fibrils and then facilitated microglial chemotaxis nearby for clearance. Simultaneously, TfPep63-Lip hindered Aβ1-42 aggregation and disaggregated Aβ1-42 assembly due to multivalent PA-Aβ. Pep63 effectively inhibited the binding between EphB2 and Aβ oligomers after release from liposomes and rescued NMDA receptors trafficking, the basis of synaptic plasticity. No side effects were observed in either APP/PS1 or wild-type mice, indicating that Tf-Pep63-Lip might be safe under the dosing regimen used in our experiment. Taken together, our results suggested that
Tf-Pep63-Lip may serve as a safe and efficient agent for AD combination therapy.
DSPE-PEG-Cy5.5是由磷脂DSPE、聚乙二醇PEG以及荧光染料Cy5.5组成。DSPE是一种高度疏水的磷脂,具有脂质双层结构,能与细胞膜相互作用;PEG具有良好的生物相容性和水溶性;Cy5.5是近红外荧光染料,在近红外区域有荧光特性。可用于生物成像和检测,如对生物样品或组织进行高分辨率成像;在化合物传递系统中,可作为表面修饰剂改善化合物分子的体内分布和稳定性,实现靶向给药和控制释放。该文献将荧光标记的DSPE-PEG-Cy5.5插入脂质体细胞膜中,获得Cy5.5-Lip和Cy5.5-Tf-Lip用于生物成像。过程如下:
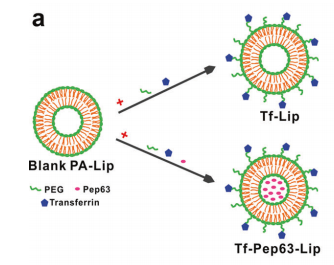
图:Tf-Lip和Tf-Pep63-Lip制备示意图。
将称取好的磷脂酸和心磷脂混合放入合适的玻璃容器中,加入适量的氯仿-甲醇混合溶剂,
使用涡旋混合器充分搅拌,使脂质完全溶解,形成透明的脂质溶液。将脂质溶液转移至旋转蒸发仪的圆底烧瓶中。在减压条件下,通过旋转蒸发仪缓慢蒸发有机溶剂。随着有机溶剂的蒸发,脂质会在烧瓶壁上形成一层均匀的薄膜。旋转速度和蒸发温度需要根据脂质的性质和溶剂的沸点进行调整,以确保薄膜的均匀性和完整性。向含有脂质薄膜的烧瓶中加入适量的缓冲液(如 PBS),缓冲液的体积根据所需脂质体的浓度和大小来确定。
让脂质薄膜在缓冲液中充分水化,通常可以在室温下轻轻搅拌数小时,使脂质薄膜逐渐从烧瓶壁上脱落,形成多层脂质体(MLV)。这个过程中,脂质分子会在缓冲液中重新排列,形成类似细胞膜的脂质双层结构。将荧光标记的DSPEPEG-Cy5.5插入脂质体细胞膜中,获得Cy5.5-Lip和Cy5.5-Tf-Lip。
制备的脂质体平均尺寸在124.83nm~135.60nm之间,PDI在0.23~0.27之间,说明脂质体具有良好的均匀性。Zeta电位值相对为负,表明阴离子PA能有效地掺入脂质体的脂膜中。小鼠体内生物成像得出结论:Tf-Pep63-Lip可降低Aβ负担。TfPep63-Lip可以捕获Aβ低聚物或原纤维,然后促进附近的小胶质细胞趋化以进行清除。同时,由于多价的PA-Aβ,TfPep63-Lip阻碍了Aβ1-42的聚集和分解Aβ1-42的组装。Pep63有效地抑制了从脂质体释放后的EphB2和Aβ低聚物之间的结合,并挽救了NMDA受体的运输。
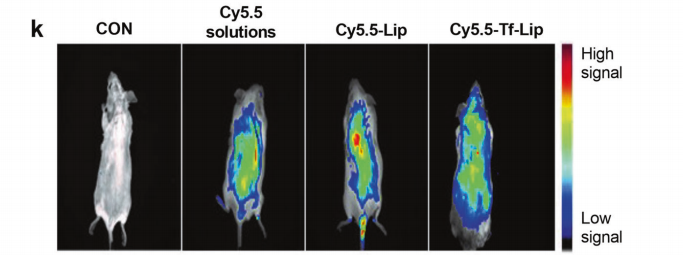
图:Cy5.5-labeled和转铁修饰脂质体在活体小鼠中的生物分布。
结论:使用DSPE-PEG-Cy5.5标记的Tf-Pep63-Lip,不仅拥有磷脂的亲脂性,能够自然嵌入到脂质体的细胞膜结构中,增强了脂质体在生物体内的可视性,能够实时追踪脂质体在细胞或生物体内的分布,还因Cy5.5的存在而具备了强烈的近红外荧光特性,非常适合用于生物成像研究。

 2025-02-14 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-14 作者:ZJ 来源:

