文献:Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Reduces Permeability and Apoptosis of Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Response to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation Followed by Reoxygenation via the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 (FGFR1)/ERK Pathway
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=100q0vh05a1t00v0ee2v0pd0b1583818&site=xueshu_se
作者:Peng Chen,Hongguang zhang,Qingtao Zhang,Wei zhou,Yongbing Deng,Xi HuLian,yang Zhang
相关产品:FITC-dextran 荧光素-葡聚糖
原文摘要:
Background:
Disruption of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a mechanism in the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. Basic
fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is expressed in angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and neuronal survival. This study
aimed to investigate the role of bFGF in vitro in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) chal
lenged by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R).
Material/Methods: HBMECs were cultured in glucose-free medium and an environment with <0.5% oxygen in an anaerobic chamber. Immunocytochemistry, Western blot, and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRTPCR) were used to measure the protein and mRNA expression levels of bFGF, tight junction, adherens junction, apoptotic proteins, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). The effects of bFGF on the viability of HBMECs was evaluated using the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Cell apoptosis was evaluated using the TUNEL assay, and endothelial permeability was quantified using a transwell migration assay with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugated with dextran. The effects of bFGF were evaluated following inhibition of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) with PD173074 and inhibition of ERK with PD98059.
Results: Following OGD/R of HBMECs, bFGF significantly reduced cell permeability and apoptosis and significantly inhibited the down-regulation of the expressions of proteins associated with tight junctions, adherens junctions, apoptosis and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). The effects of bFGF were mediated by the activation of FGFR1 and ERK, as they were blocked by FGFR1 and ERK inhibitors.
Conclusions: Permeability and apoptosis of HBMECs challenged by OGD/R were reduced by bFGF by activation of the FGFR1 and the ERK pathway.
FITC-dextran 是将荧光素异硫氰酸酯(FITC)与葡聚糖共价连接形成的化合物。葡聚糖是一类由葡萄糖以糖苷键连接而成的具支链高聚物。可用于细胞和组织成像,研究细胞的内吞、胞吐或细胞膜的通透性;在微循环和细胞通透性研究中是重要的工具;在生物医学领域,可作为生物成像剂。此篇引用的文献研究探讨FITC-dextran成像后,bFGF体外受氧-葡萄糖剥夺/再灌注OGD/R在HBMECs中的作用。
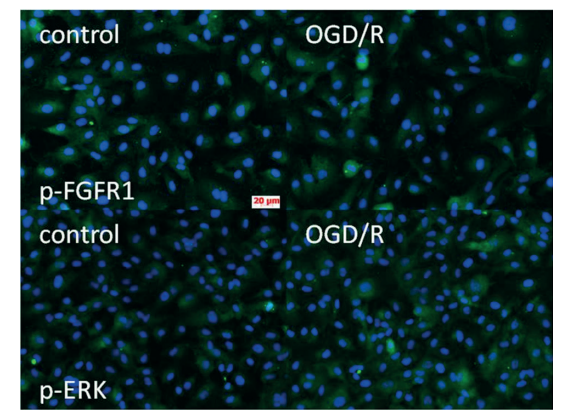
图:HBMECs中p-FGFR1和p-ERK的免疫荧光染色显示
方法:HBMECs在无糖培养基和<0.5%氧环境中培养。采用免疫细胞化学、Western blot和定量逆转录-聚合酶链反应(qRTPCR)检测bFGF、紧密连接、粘附连接、Apoptosis 蛋白和基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)的蛋白和mRNA表达水平。采用细胞计数试剂盒-8(CCK-8)检测bFGF对HBMECs活力的影响。使用TUNEL法评估细胞Apoptosis ,并使用FITC-dextran结合的跨孔迁移试验定量内皮细胞的通透性。在PD173074抑制成纤维细胞生长因子受体1(FGFR1),PD98059抑制ERK后,评估bFGF的作用。
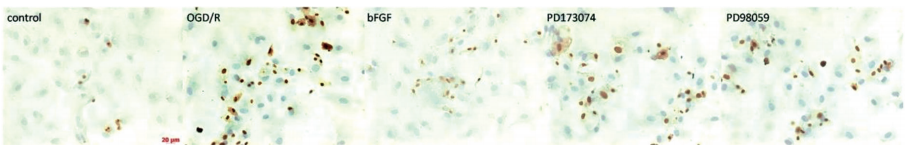
图:OGD/R后12 hApoptosis 细胞免疫染色,TUNEL检测
结论:FITC-dextran参与bFGF体外受氧-葡萄糖HBMECs OGD/R后,bFGF降低细胞通透性,抑制紧密连接、粘附连接和基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)相关蛋白表达的下调。bFGF的作用是通过FGFR1和ERK的激活来介导的,因为它们被FGFR1和ERK抑制剂所阻断。

 2025-02-13 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-13 作者:ZJ 来源:

