文献:Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide)-Monomethoxy-Poly-(Polyethylene Glycol) Nanoparticles Loaded with Melatonin Protect Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Transplanted in Infarcted Heart Tissue
作者:QIANG MA , JUNJIE YANG, XU HUANG,WEISHENG GUO, SULEI LI, HAO ZHOU,JINGWEI LI, FENG CAO, YUNDAI CHEN
相关产品:PLGA15000-mPEG5000 聚乳酸羟基乳酸共聚物15000-甲氧基聚乙二醇5000
原文摘要:Stem cell transplantation is a promising therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. However, transplanted cells face low survival rates due to oxidative stress and the inflammatory microenvironment in ischemic heart tissue. Melatonin has been used as a powerful endogenous antioxidant to protect cells from oxidative injury. However, melatonin cannot play a long-lasting effect against the hostile microenvironment. Nano drug delivery carriers have the ability to protect the loaded drug from degradation in physiological environments in a controlled manner, which results in longer effects and decreased side effects. Therefore, we constructed poly(lactide-coglycolide)-monomethoxy-poly-(polyethylene glycol) (PLGA-mPEG) nanoparticles to encapsulate melatonin. We tested whether the protective effect of melatonin encapsulated by PLGA-mPEG nanoparticles (melatonin nanoparticles [Mel-NPs]) on adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) was enhanced compared to that of free melatonin both in vitro and in vivo. In the in vitro study, we found that Mel-NPs reduced formation of the p53- cyclophilin D complex, prevented mitochondrial permeability transition pores from opening, and rescued ADSCs from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Moreover, Mel-NPs can achieve higher ADSC survival rates than free melatonin in rat myocardial infarction areas, and the therapeutic effects of ADSCs pretreated
with Mel-NPs were more apparent. Hence, the combination of Mel-NPs and stem cell transplan
tation may be a promising strategy for myocardial infarction therapy.
PLGA15000-mPEG5000是由聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA)和甲氧基聚乙二醇(mPEG)组成的聚合物材料。PLGA部分具有良好的生物可降解性和生物相容性。其降解产物为乳酸和羟基乙酸,可安全地在体内代谢。mPEG部分甲氧基的封端使得它在一端具有稳定性,同时聚乙二醇链赋予了整个材料良好的亲水性。这种亲水性可以有效降低材料与生物体内环境之间的非特异性相互作用,减少蛋白质吸附等现象。用于包裹疏水性化合物,提高化合物的溶解度和稳定性,实现化合物的长效缓释。基于以上性质本文构建了PLGA-mPEG纳米颗粒来包封Mel。过程如下:

图:用透射电镜观察到的Mel-NPs纳米粒子的形貌。
Mel-NPs纳米颗粒的制备
采用薄膜水化法制备了Mel-NPs。PLGA15000-mPEG5000溶解在丙酮/氯仿混合物中,然后加入Mel。混合物搅拌,转移到连接到旋转蒸发器的蒸发器烧瓶中。在真空下开始蒸发后干燥混合物在蒸发器烧瓶中形成薄膜。将膜样产品溶解在双蒸馏水中,用浴式超声器分散,形成Mel-NPs。用无菌过滤器过滤,冷冻干燥。
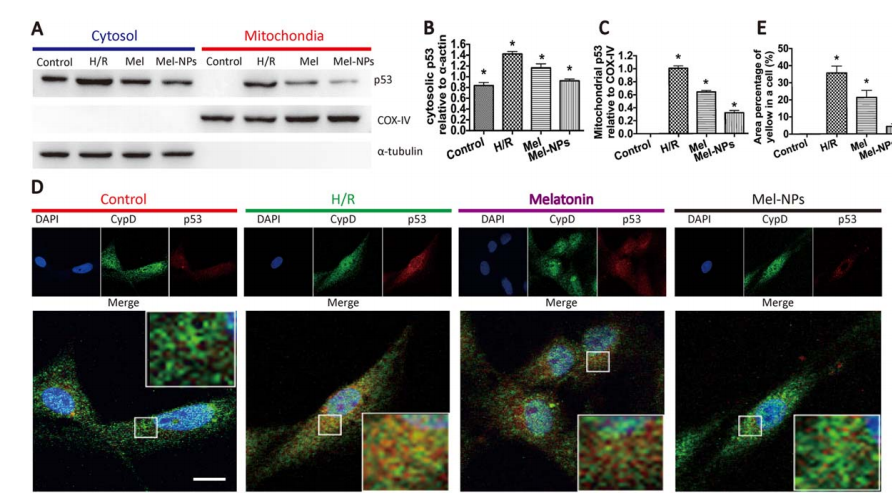
图:Mel-NPs抑制p53-CypD复合物的形成
结论:基于PLGA15000-mPEG5000 构建的PLGA-mPEG纳米颗粒来包封Mel,Mel-NPs减少了p53-亲环素D复合物的形成,阻止了线粒体通透性过渡孔的打开,并使ADSCs免于缺氧/再氧损伤。此外,Mel-NPs可比游离melatonin获得更高的ADSC存活率,且经Mel-NPs预处理的ADSCs的效果更为明显。

 2025-02-13 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-13 作者:ZJ 来源:

